Статьи журнала «Институт Стоматологии» (стр.107)
Резюме. Сравнительный анализ информативности цифровой микрофокусной рентгенографии с многократным увеличением изображения и радиовизиографии при эндодонтическом лечении в эксперименте продемонстрировал наибольшую информативность цифровой микрофокусной рентгенографии с увеличением в 5-7 раз. Применение цифровой микрофокусной рентгенографии с многократным увеличением при планировании и проведении эндодонтического лечения многокорневых зубов, за счет эффекта псевдообъема позволяет уменьшить количество необходимых исследований, упростить процедуру позиционирования во время исследования, а также интерпретацию результатов.
Ключевые слова: эндодонтическое лечение, микрофокусная рентгенография, радиовизиография, псевдообъем.
Comparative estimation of the information value digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification in the image and digital radiography in experiment (V.G. Alpatova, А.U. Vasilev, L.P. Kiselnikova, N.N. Potrahov, A.U.Gryaznov, A.S.Selyagina, V. Petrovskaya).
Summary. Comparative estimation of the information value digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification in the image and digital radiography during endodontic treatment in experiment has shown the greatest informativity of the digital microfocus radiography with 5-7 × magnification. Application digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification at planning and carrying out root canal treatment of the multirooted teeth allows to reduce quantity of necessary researches, to simplify procedure of positioning during research, and also interpretation of results due to effect of pseudo-volume.
Key words: еndodontic (root canal) treatment, microfocus radiography, digital radiography, pseudo-volume.
Литература:
1. Васильев А.Ю., Буланова И.М., Потрахов Н.Н.Микрофокусная рентгенография: современное состояние и перспективы //Вестник рентгенологии и радиологии. - 2007. - №1. - С. 55-59.
2. Коуэн С. Эндодонтия: Пер. с англ. / С.Коуэн, Р.Бернс - СПб: НПО “Мир и семья - 95”; ООО “Интерлайн”, 2000.- 696 с.
3. Петрикас А.Ж. Строение зуба и пародонта / А.Ж.Петрикас, В.А.Соловьев, О.В.Мансурский // Клинич. стоматология. - 1998. - №4. - С. 30-32.
4. Предтеченский А.Г. Внутриротовой снимок. Классическая рентгенография в стоматологии. // Стоматология сегодня - 2001. - № 4. - С. 7.
5. Рабухина Н.А. Роль рентгенологического исследования при эндодонтическом и хирургическом лечении зубов / Н.А.Рабухина, Л.А.Григорьянц, В.А.Бадалян // Новое в стоматологии. - 2001. - №6. - С. 39-41.
6. Чибисова М.А., Дударев А.Л., Березкин Д.А. Малодозовая цифровая полипозиционная дентальная рентгенография //Институт Стоматологии. - 2004. - №3 (24). - С. 111-113.
7. Buckland-Wright J.C.. Clinical applications of highdefinition microfocal radiography// British Journal of Radiology (1989) 62, 209-217.
8. Danforth R.A., Torabainejad M. Evaluation of radiation risk associated with endodontic radiography. J Ital Endod 1991; 5: 1: 18-22.
9. Pаsler F.A., Visser H. Рентгенодиагностика в практике стоматолога. / Пер. с нем. Под общ. ред. Н.А.Рабухиной. М: МЕД-пресс-информ. - 2007.
10. Takahashi S. & Sakuma S. Magnification Radiography // Japanese Journal of Radiological Technology, 1975, 31(6) pp. 601.
Ключевые слова: эндодонтическое лечение, микрофокусная рентгенография, радиовизиография, псевдообъем.
Comparative estimation of the information value digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification in the image and digital radiography in experiment (V.G. Alpatova, А.U. Vasilev, L.P. Kiselnikova, N.N. Potrahov, A.U.Gryaznov, A.S.Selyagina, V. Petrovskaya).
Summary. Comparative estimation of the information value digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification in the image and digital radiography during endodontic treatment in experiment has shown the greatest informativity of the digital microfocus radiography with 5-7 × magnification. Application digital microfocus radiography with multiple magnification at planning and carrying out root canal treatment of the multirooted teeth allows to reduce quantity of necessary researches, to simplify procedure of positioning during research, and also interpretation of results due to effect of pseudo-volume.
Key words: еndodontic (root canal) treatment, microfocus radiography, digital radiography, pseudo-volume.
Литература:
1. Васильев А.Ю., Буланова И.М., Потрахов Н.Н.Микрофокусная рентгенография: современное состояние и перспективы //Вестник рентгенологии и радиологии. - 2007. - №1. - С. 55-59.
2. Коуэн С. Эндодонтия: Пер. с англ. / С.Коуэн, Р.Бернс - СПб: НПО “Мир и семья - 95”; ООО “Интерлайн”, 2000.- 696 с.
3. Петрикас А.Ж. Строение зуба и пародонта / А.Ж.Петрикас, В.А.Соловьев, О.В.Мансурский // Клинич. стоматология. - 1998. - №4. - С. 30-32.
4. Предтеченский А.Г. Внутриротовой снимок. Классическая рентгенография в стоматологии. // Стоматология сегодня - 2001. - № 4. - С. 7.
5. Рабухина Н.А. Роль рентгенологического исследования при эндодонтическом и хирургическом лечении зубов / Н.А.Рабухина, Л.А.Григорьянц, В.А.Бадалян // Новое в стоматологии. - 2001. - №6. - С. 39-41.
6. Чибисова М.А., Дударев А.Л., Березкин Д.А. Малодозовая цифровая полипозиционная дентальная рентгенография //Институт Стоматологии. - 2004. - №3 (24). - С. 111-113.
7. Buckland-Wright J.C.. Clinical applications of highdefinition microfocal radiography// British Journal of Radiology (1989) 62, 209-217.
8. Danforth R.A., Torabainejad M. Evaluation of radiation risk associated with endodontic radiography. J Ital Endod 1991; 5: 1: 18-22.
9. Pаsler F.A., Visser H. Рентгенодиагностика в практике стоматолога. / Пер. с нем. Под общ. ред. Н.А.Рабухиной. М: МЕД-пресс-информ. - 2007.
10. Takahashi S. & Sakuma S. Magnification Radiography // Japanese Journal of Radiological Technology, 1975, 31(6) pp. 601.
| Авторы: | Алпатова Виктория Георгиевна, Васильев А.Ю., Кисельникова Лариса Петровна, Потрахов Н.Н., Грязнов А.Ю., Селягина А.С., Петровская В.В. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 80-81 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В комплексном лечении ХГ П применен 3% раствор препарата люцерны посевной методом аппликации и ультрафонофореза. К концу курса лечения достоверно улучшились иммунологические показатели РЖ, нормализовалась антиоксидантная защита полости рта и кровоснабжение тканей пародонта.
Ключевые слова: хронический генерализованный пародонтит, люцерна посевная, комплексное лечение.
Аlfalfa application in complex treatment of chronic generalized parodontitis (F.Z.Mirsaeva, L.A.Farvazova, L.F.Gubaidullina, E.I.Galieva, L.A.Ryabykh).
Summary. 3% Solutio Alfalfa has been applied in care of complex treatment of chronic generalized parodontitis in the form of application and ultraphonophoresis. Immullogic findings of mouth liquids were sure to be improved. Antioxide mouth cavity defence has been normalized and parodont tissues blood streem has been improved.
Key words: chronic generalized periodontitis, Alfalfa, complex treatment.
Литература:
1. Барер Г.М., Лемецкая Т.И. Болезни пародонта: клиника, диагностика и лечение. - М., 1996. - 86 с.
2. Грудянов А.И. Пародонтология (избранные лекции). - М., 1997. - 35 с.
3. Грудянов А.И., Москалев К.Е. Биохимические исследования различных физиологических средств и тканей при воспалительных заболеваниях пародонта (лит. обзор) // Пародонтология. - 1997. - №4. - С. 3-13.
4. Дубинина Е.Е., Сальникова Л.А., Ефимова Л.Ф. Активность и изоферментный спектр супероксиддисмутазы эритроцитов в плазме крови человека // Лаб. дело. - 1983. - №10. - С. 30-32.
5. Меджитов М.Н. Оценка эффективности использования препаратов тромбоцитарного фактора роста - ББ и системы фибрин-фибронектина в хирургическом лечении локальной рецессии десны / М.Н. Меджитов, Л.А.Дмитриева // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №2. - С. 62-64.
6. Стальная И.Д., Гаришвили Т.Г., Метод определения малонового диальдегида с помощью тиобарбитуровой кислоты // Современные методы в биохимии. - М., 1977. - С. 66-68.
Ключевые слова: хронический генерализованный пародонтит, люцерна посевная, комплексное лечение.
Аlfalfa application in complex treatment of chronic generalized parodontitis (F.Z.Mirsaeva, L.A.Farvazova, L.F.Gubaidullina, E.I.Galieva, L.A.Ryabykh).
Summary. 3% Solutio Alfalfa has been applied in care of complex treatment of chronic generalized parodontitis in the form of application and ultraphonophoresis. Immullogic findings of mouth liquids were sure to be improved. Antioxide mouth cavity defence has been normalized and parodont tissues blood streem has been improved.
Key words: chronic generalized periodontitis, Alfalfa, complex treatment.
Литература:
1. Барер Г.М., Лемецкая Т.И. Болезни пародонта: клиника, диагностика и лечение. - М., 1996. - 86 с.
2. Грудянов А.И. Пародонтология (избранные лекции). - М., 1997. - 35 с.
3. Грудянов А.И., Москалев К.Е. Биохимические исследования различных физиологических средств и тканей при воспалительных заболеваниях пародонта (лит. обзор) // Пародонтология. - 1997. - №4. - С. 3-13.
4. Дубинина Е.Е., Сальникова Л.А., Ефимова Л.Ф. Активность и изоферментный спектр супероксиддисмутазы эритроцитов в плазме крови человека // Лаб. дело. - 1983. - №10. - С. 30-32.
5. Меджитов М.Н. Оценка эффективности использования препаратов тромбоцитарного фактора роста - ББ и системы фибрин-фибронектина в хирургическом лечении локальной рецессии десны / М.Н. Меджитов, Л.А.Дмитриева // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №2. - С. 62-64.
6. Стальная И.Д., Гаришвили Т.Г., Метод определения малонового диальдегида с помощью тиобарбитуровой кислоты // Современные методы в биохимии. - М., 1977. - С. 66-68.
| Авторы: | Мирсаева Ф.З., Фарвазова Л.А., Губайдуллина Л.Ф., Галиева Э.И., Рябых Л.А. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 78-79 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Наличие микроциркуляторных нарушений пародонтального комплекса является доминирующим фактором в развитииосложнений воспалительной природы у лиц с ДСТ . Анализ результатов ЛД Ф показал, что онявляется методом выбора при осуществлении контроля над состоянием микроциркуляции, позволяющим контролировать коррекцию микрогемодинамических расстройств при различных патологических состояниях пародонта. Это позволит резко повысить результаты и сократить сроки лечения этой категории больных.
Ключевые слова: дисплазия соединительной ткани, пародонтит, регенерация.
Functional estimation of the conditionmicrocirculation beside patient with chronicperiodontitis on background mesenchimal reparationals (V.P.Konev, T.V.Suncova, E.G.Kirova).
Summary. Presence microcirculation breaches periodontitis complex is a dominant factor in development of the complications of the inflammatory nature beside persons with mesenchimal reparationals Analysis result LDF has shown that he is a method of the choice at realization of the checking on condition microcirculation, allowing check correction an микрогемодинамических frustration under different pathological conditions periodont. This will allow sharply to raise the results and reduce the time of the treatment to this categories sick.
Key words: mesenchimal reparationals, periodontitis, regeneration.
ЛИТЕРАТУРА:
1. Бобырев В.Н., Розколупа Н.В., Скрипникова Т.Н. Экспериментальные иклинические основы применения антиоксидантов как средств лечения и профилактики пародонтита // Стоматология. - 1994. - №3. - С. 11-18.
2. Григорович Э.Ш. Морфофункциональная характеристика органов и тканейполости рта у лиц с недифференцированными дисплазиями соединительной ткани: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук / Э.Ш. Григорович - Омск. - 2003. - 23 с.
3. Грудянов А.И. Пародонтология // Избр. лекции.- М. - 1997. - С. 32.
4. Канканян А.П., Леонтьев В.К. Болезни пародонта: Новые подходы в этиологии, патогенезе, профилактике и лечении. - Ереван: Тигран Мец. - 1998. - 360 с.
5. Нимаев Б.Ц. Пути оптимизации лечения больных с переломами нижней челюсти на фоне дисплазии соединительной ткани: Автореф. ... к.м.н. 14.00.21. ОГМА . - Омск. - 2000. - 21 с.
6. Н изкочастотный ультразвук в стоматологии / Педдер В.В., Иванова Г.Г., Ивасенко П.И. и др.: Методические рекомендации. - Омск. - 2001. - 110 с.
7. Сулимов А.Ф., Ивасенко П.И., Савченко Р.К. Врожденная дисплазия соединительной ткани и ее проявления в челюстно-лицевой области (методические рекомендации).- Омск. - 2001. - 25 с.
8. Яковлев В.М. Кардиореспираторные синдромы при дисплазии соединительной ткани / В.М. Яковлев, Г.И. Нечаева // Омск.: ОГМА . - 1994. - 217 с.
Ключевые слова: дисплазия соединительной ткани, пародонтит, регенерация.
Functional estimation of the conditionmicrocirculation beside patient with chronicperiodontitis on background mesenchimal reparationals (V.P.Konev, T.V.Suncova, E.G.Kirova).
Summary. Presence microcirculation breaches periodontitis complex is a dominant factor in development of the complications of the inflammatory nature beside persons with mesenchimal reparationals Analysis result LDF has shown that he is a method of the choice at realization of the checking on condition microcirculation, allowing check correction an микрогемодинамических frustration under different pathological conditions periodont. This will allow sharply to raise the results and reduce the time of the treatment to this categories sick.
Key words: mesenchimal reparationals, periodontitis, regeneration.
ЛИТЕРАТУРА:
1. Бобырев В.Н., Розколупа Н.В., Скрипникова Т.Н. Экспериментальные иклинические основы применения антиоксидантов как средств лечения и профилактики пародонтита // Стоматология. - 1994. - №3. - С. 11-18.
2. Григорович Э.Ш. Морфофункциональная характеристика органов и тканейполости рта у лиц с недифференцированными дисплазиями соединительной ткани: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук / Э.Ш. Григорович - Омск. - 2003. - 23 с.
3. Грудянов А.И. Пародонтология // Избр. лекции.- М. - 1997. - С. 32.
4. Канканян А.П., Леонтьев В.К. Болезни пародонта: Новые подходы в этиологии, патогенезе, профилактике и лечении. - Ереван: Тигран Мец. - 1998. - 360 с.
5. Нимаев Б.Ц. Пути оптимизации лечения больных с переломами нижней челюсти на фоне дисплазии соединительной ткани: Автореф. ... к.м.н. 14.00.21. ОГМА . - Омск. - 2000. - 21 с.
6. Н изкочастотный ультразвук в стоматологии / Педдер В.В., Иванова Г.Г., Ивасенко П.И. и др.: Методические рекомендации. - Омск. - 2001. - 110 с.
7. Сулимов А.Ф., Ивасенко П.И., Савченко Р.К. Врожденная дисплазия соединительной ткани и ее проявления в челюстно-лицевой области (методические рекомендации).- Омск. - 2001. - 25 с.
8. Яковлев В.М. Кардиореспираторные синдромы при дисплазии соединительной ткани / В.М. Яковлев, Г.И. Нечаева // Омск.: ОГМА . - 1994. - 217 с.
| Авторы: | Сунцова Т.В., Кирова Е.Г. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 76-77 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме: У детей с нарушениями опорно-двигательного аппарата с ЗЧАД преобладает глубокая резцовая окклюзия, дистальная окклюзия инейтральная окклюзия с аномалиями отдельных зубов. Причем с возрастанием степени тяжести нарушений опорно-двигательного аппарата (от нарушения осанки к сколиозу III-IV степени тяжести) возрастает распространенность дистальной окклюзии.
Ключевые слова: зубочелюстные аномалии и деформации, нарушения опорно-двигательного аппарата, нарушение осанки, сколиоз.
Characteristic of childrens dentoalveolaranomalies and deformities with various state of locomotor apparatus (E.G.Perova, Аssosiate professor; A.A.Levenets, рrofessor).
Summary: Deep incisor occlusion, distal occlusion and neutral occlusion with anomalies of individual teeth are prevalent among children with locomotor apparatus abnormalities and dentoalveolar anomalies and deformities. More over, with increasing the degree of severity of locomotor apparatus abnormalities (Srom irregular bearing to scoliosis of the third and the forth degrees of severity) prevalence of distal occlusion is rising.
Key words: dentoalveolar anomalies and deformities, locomotor apparatus abnormalities, irregular bearing, scoliosis.
Литература:
1. Алимский А.В. Возрастная динамика роста распространенности и изменения структуры аномалийсреди дошкольников и школьников / А.В.Алимский // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 5. - С. 67-71.
2. Гасымова З.В. Взаимосвязь зубочелюстно-лицевых аномалий с ротовым дыханием, нарушенной осанкой и способы комплексного лечения / З.В.Гасымова // Стоматология. - 2003. - № 1. - С. 22- 25.
3. Даминов Т.О. Роль общих факторов в патогенезе развития деформаций зубочелюстной системы у детей / Т.О.Даминов, Р.К.Якубов, И.Р.Мавлянов и др. // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 4. - С. 57 - 60.
4. Манин А.И. Распространенность аномалий зубов у жителей различных регионов России / А.И.Манин, М.В.Ретинская, В.П.Тачиева и др. // Ортодонтия. - 2003. - № 4. - С. 9-12.
5. Проскокова С.В. Распространенность зубочелюстных аномалий и деформаций у детей г.Хабаровска и Хабаровского района, находившихся под воздействием экологически неблагоприятных факторов / С.В.Проскокова // Ортодонтия. - 2007. - №4 (40). - С. 6-7.
6. Проффит У.Р. Современная ортодонтия / У.Р.Проффит (под ред. чл.-корр. РАМН , проф. Персина Л.С.). - М., “МЕДпресс-информ, 2006. - 559 с.
7. Хорошилкина Ф.Я. Нарушение осанки при аномалиях прикуса / Ф.Я.Хорошилкина // Ортодент-Инфо. - 2000. - № 1-2. - С. 40-47.
8. Цимбалистов А.В. Динамика стабилометрических характеристик на этапах ортодонтического лечения дистальной окклюзии у больных с нарушениями опорно-двигательного аппарата / А.В.Цимбалистов,Т.А.Лопушанская, Е.Я.Худоногова и др. // Ортодонтия. - 2005. - № 3. - С. 21 - 24.
9. Hirschfelder H., Hirschfelder U. Sagittale Kieferrelation und Wirbetsaulenhaltung: Untersuchung zur Frage einer Abhangigkeit. Forschr. Kieferorthop.1987; 48: 436-48.
10. Huggare J. Postural disordes and dentofacial morphology. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1998; 21: 12-19.
Ключевые слова: зубочелюстные аномалии и деформации, нарушения опорно-двигательного аппарата, нарушение осанки, сколиоз.
Characteristic of childrens dentoalveolaranomalies and deformities with various state of locomotor apparatus (E.G.Perova, Аssosiate professor; A.A.Levenets, рrofessor).
Summary: Deep incisor occlusion, distal occlusion and neutral occlusion with anomalies of individual teeth are prevalent among children with locomotor apparatus abnormalities and dentoalveolar anomalies and deformities. More over, with increasing the degree of severity of locomotor apparatus abnormalities (Srom irregular bearing to scoliosis of the third and the forth degrees of severity) prevalence of distal occlusion is rising.
Key words: dentoalveolar anomalies and deformities, locomotor apparatus abnormalities, irregular bearing, scoliosis.
Литература:
1. Алимский А.В. Возрастная динамика роста распространенности и изменения структуры аномалийсреди дошкольников и школьников / А.В.Алимский // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 5. - С. 67-71.
2. Гасымова З.В. Взаимосвязь зубочелюстно-лицевых аномалий с ротовым дыханием, нарушенной осанкой и способы комплексного лечения / З.В.Гасымова // Стоматология. - 2003. - № 1. - С. 22- 25.
3. Даминов Т.О. Роль общих факторов в патогенезе развития деформаций зубочелюстной системы у детей / Т.О.Даминов, Р.К.Якубов, И.Р.Мавлянов и др. // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 4. - С. 57 - 60.
4. Манин А.И. Распространенность аномалий зубов у жителей различных регионов России / А.И.Манин, М.В.Ретинская, В.П.Тачиева и др. // Ортодонтия. - 2003. - № 4. - С. 9-12.
5. Проскокова С.В. Распространенность зубочелюстных аномалий и деформаций у детей г.Хабаровска и Хабаровского района, находившихся под воздействием экологически неблагоприятных факторов / С.В.Проскокова // Ортодонтия. - 2007. - №4 (40). - С. 6-7.
6. Проффит У.Р. Современная ортодонтия / У.Р.Проффит (под ред. чл.-корр. РАМН , проф. Персина Л.С.). - М., “МЕДпресс-информ, 2006. - 559 с.
7. Хорошилкина Ф.Я. Нарушение осанки при аномалиях прикуса / Ф.Я.Хорошилкина // Ортодент-Инфо. - 2000. - № 1-2. - С. 40-47.
8. Цимбалистов А.В. Динамика стабилометрических характеристик на этапах ортодонтического лечения дистальной окклюзии у больных с нарушениями опорно-двигательного аппарата / А.В.Цимбалистов,Т.А.Лопушанская, Е.Я.Худоногова и др. // Ортодонтия. - 2005. - № 3. - С. 21 - 24.
9. Hirschfelder H., Hirschfelder U. Sagittale Kieferrelation und Wirbetsaulenhaltung: Untersuchung zur Frage einer Abhangigkeit. Forschr. Kieferorthop.1987; 48: 436-48.
10. Huggare J. Postural disordes and dentofacial morphology. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1998; 21: 12-19.
| Авторы: | Перова Е.Г., Левенец А.А. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 74-75 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
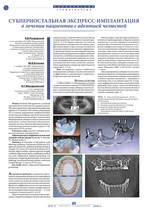
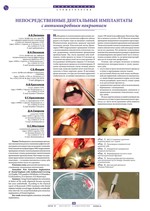
PDF)Резюме. В лечении 206 пациентов с тотальной адентией обеих челюстей (22), верхней челюсти (95), односторонними и двусторонними дефектами верхнего (57), нижнего (23) и обоих зубных рядов (9) в условиях выраженной атрофии беззубых сегментов альвеолярных отростков использован метод субпериостальной экспресс-имплантации. Моделирование субпериостальных имплантатов выполняли с учетом патологии зубочелюстнолицевой системы. Хорошие функциональные и эстетические результаты лечения в сроки 3-5 лет получены в 97,1% случаях.
Ключевые слова: адентия, субпериостальная имплантация, моделирование.
Subperiostal express-implantation in treat-ment of patients with jaw adentia (Razdorsky V., Kotenko M., Mackaryevsky I.)
Summary. In treatment of 206 patients with following conditions: total adentia of both jaws (22), upper jaw adentia (95), unilateral and bilateral defects of upper (57), lower (23) and both dentitions (9) in alveolar ridges toothless segment apparent atrophy conditions subperiostal express-implantation method was used. Subperiostal implants positioning was performed considering dentoalveolar-facial system pathology. Good functional and aesthetic results were reached during 3-5 years in 97.1% cases.
Key words: adentia, subperiostal implantation, positioning.
Литература:
1. Бессонов В.И., Российский П.В. Субпериостальная имплантация: Лечение, возможные осложнения, отдаленные результаты // Клиническая имплантология и стоматология. - 2001. - № 1-2. - С. 41-43.
2. Костная пластика в стоматологической имплантологии. Описание методик и их клиническое применение / под ред. Ф.Ф. Альфаро.М: Азбука, 2006. - 235 с.
3. Суров О.Н. Зубное протезирование на имплантатах М.: Медицина, 1993. - 204 с.
4. Суров О. Ренессанс субпериостальной имплантации? // Новое в стоматологии. - 2009. -№ 1 (157). - С. 1-5.
5. Суров О. Современная практика субпериостальной имплантации // Новое в стоматологии. - 2009. - № 4 (160). - С. 1-26.
6. Хватова В.А. Клиническая гнатология. М.: Москва, 2005. - 295 с.
7. Ховат А.П., Джей Капп Н., Джей Барретт Н.В. Окклюзия и патология окклюзии. М.: Азбука, 2005. - 235 с.
8. Weiss Ch. M., Weiss A. Principles and practice of implant dentistry. St. Louis: Mosby, 2001. 447 p.
Ключевые слова: адентия, субпериостальная имплантация, моделирование.
Subperiostal express-implantation in treat-ment of patients with jaw adentia (Razdorsky V., Kotenko M., Mackaryevsky I.)
Summary. In treatment of 206 patients with following conditions: total adentia of both jaws (22), upper jaw adentia (95), unilateral and bilateral defects of upper (57), lower (23) and both dentitions (9) in alveolar ridges toothless segment apparent atrophy conditions subperiostal express-implantation method was used. Subperiostal implants positioning was performed considering dentoalveolar-facial system pathology. Good functional and aesthetic results were reached during 3-5 years in 97.1% cases.
Key words: adentia, subperiostal implantation, positioning.
Литература:
1. Бессонов В.И., Российский П.В. Субпериостальная имплантация: Лечение, возможные осложнения, отдаленные результаты // Клиническая имплантология и стоматология. - 2001. - № 1-2. - С. 41-43.
2. Костная пластика в стоматологической имплантологии. Описание методик и их клиническое применение / под ред. Ф.Ф. Альфаро.М: Азбука, 2006. - 235 с.
3. Суров О.Н. Зубное протезирование на имплантатах М.: Медицина, 1993. - 204 с.
4. Суров О. Ренессанс субпериостальной имплантации? // Новое в стоматологии. - 2009. -№ 1 (157). - С. 1-5.
5. Суров О. Современная практика субпериостальной имплантации // Новое в стоматологии. - 2009. - № 4 (160). - С. 1-26.
6. Хватова В.А. Клиническая гнатология. М.: Москва, 2005. - 295 с.
7. Ховат А.П., Джей Капп Н., Джей Барретт Н.В. Окклюзия и патология окклюзии. М.: Азбука, 2005. - 235 с.
8. Weiss Ch. M., Weiss A. Principles and practice of implant dentistry. St. Louis: Mosby, 2001. 447 p.
| Авторы: | Раздорский В.В., Котенко М.В., Макарьевский И.Г. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 72-73 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Комплексное исследование защитных системполости рта больных пожилого и старческого возраста с сердечно-сосудистой патологией и хроническим генерализованным пародонтитом выявило существенные изменения в иммунитете, гемостазе, гомоцистеиновом обмене. Включение в традиционную терапию Вилона оказывает выраженный благоприятный эффект.
Ключевые слова: слюна, иммунитет, гомоцистеин.
Vilon influence on local protective factorsof mouth cavity in senile and elder age patients (Y.I. Pinelis, Chita state medical academy).
Summary. Complex study of mouth cavity protective systems in senile and elder age patients with cardiac pathology and chronic generalized parodontitis revealed essential immunity, hemostasis and homocystein exchange changes. Traditional therapy with Vilon introduction shows marked favorable effect.
Key words: saliva, immunity, homocystein.
Литература:
1. Алимский А.В. Геронтостоматология: настоящее и перспективы / А.В.Алимский // Стоматология для всех. - 1999. - №1. - С. 29-31.
2. Беленков Ю.Н. Национальные рекомендации по диагностике и лечению хронической сердечной недостаточности / Ю.Н.Беленков, В.Ю.Мареев, Ф.Т.Агеев // Сердечная недостаточность. - 2002. - №6. - С. 3-8.
3. Горбачева И.А. Окислительный стресс и его особенностиу больных генерализованным пародонтитом на фоне заболеваний внутренних органов / И.А.Горбачева, А.И.Кирсанов, Л.Ю.Орехова // Пародонтология. - 2002. - № 4. - С. 3-7.
4. Орехова Л.Ю. Иммунологические механизмы в патогенезе воспалительных заболеваний пародонта: Автореф. дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - СПб. - 1997. - 34 с.
5. Barkagan Z.S. Diagnosis and controlled therapy of hemostasis injure / Z.S.Barkagan, A.P. Momot. - M. - Nyudiamed. - 2001. - 296 p.
6. Kirkowood T.B. Evolution, stress, and longevity // J. Anat.-2000. - №2. - P. 296.
7. Rich M.W. “Heart failure in the elderly: strategies to optimize outpatient control and reduce hospitalizations”. Am J. Geriatr. Cardiol, 2003 12(1):19-27.
8. WNO: Epidemiology, etiology and prevention of periodontal disease // Technical. Repot. Series. Geneva. - 1978. - № 62. - P. 60.
Ключевые слова: слюна, иммунитет, гомоцистеин.
Vilon influence on local protective factorsof mouth cavity in senile and elder age patients (Y.I. Pinelis, Chita state medical academy).
Summary. Complex study of mouth cavity protective systems in senile and elder age patients with cardiac pathology and chronic generalized parodontitis revealed essential immunity, hemostasis and homocystein exchange changes. Traditional therapy with Vilon introduction shows marked favorable effect.
Key words: saliva, immunity, homocystein.
Литература:
1. Алимский А.В. Геронтостоматология: настоящее и перспективы / А.В.Алимский // Стоматология для всех. - 1999. - №1. - С. 29-31.
2. Беленков Ю.Н. Национальные рекомендации по диагностике и лечению хронической сердечной недостаточности / Ю.Н.Беленков, В.Ю.Мареев, Ф.Т.Агеев // Сердечная недостаточность. - 2002. - №6. - С. 3-8.
3. Горбачева И.А. Окислительный стресс и его особенностиу больных генерализованным пародонтитом на фоне заболеваний внутренних органов / И.А.Горбачева, А.И.Кирсанов, Л.Ю.Орехова // Пародонтология. - 2002. - № 4. - С. 3-7.
4. Орехова Л.Ю. Иммунологические механизмы в патогенезе воспалительных заболеваний пародонта: Автореф. дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - СПб. - 1997. - 34 с.
5. Barkagan Z.S. Diagnosis and controlled therapy of hemostasis injure / Z.S.Barkagan, A.P. Momot. - M. - Nyudiamed. - 2001. - 296 p.
6. Kirkowood T.B. Evolution, stress, and longevity // J. Anat.-2000. - №2. - P. 296.
7. Rich M.W. “Heart failure in the elderly: strategies to optimize outpatient control and reduce hospitalizations”. Am J. Geriatr. Cardiol, 2003 12(1):19-27.
8. WNO: Epidemiology, etiology and prevention of periodontal disease // Technical. Repot. Series. Geneva. - 1978. - № 62. - P. 60.
| Авторы: | Пинелис Ю.И. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 71 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Причинами локализованного пародонтита травматической этиологии являются дефектные пломбы, коронки с отсутствующим экватором и вредные привычки (интенсивное использование инородных предметов для очищения промежутка между зубами). При комплексном лечении локализованного пародонтита травматической этиологии наиболее важным звеном является применение шинирующих ортопедических конструкций. Основной задачей такого лечения является устранение травматического фактора пародонтального кармана и создание условий для последующей регенерации тканей пародонта.
Ключевые слова: локализованный пародонтит, комплексное лечение пародонтита.
Сomplex management of local periodontitis of traumatic origin (A.V.Smirnova, B.T.Moroz).
Summary. Problems with restaurations, nonanatomical dental crowns without proximal points and harmful habits are counted the main causes of local periodontitis of traumatic origin. The prosthodontic methods are the most important part in multiple treatment of local periodontitis. The complex management of local periodontitis of traumatic origin is based on stopping of traumatic factor and defence of periodontal pocket for the subsequent regeneration.
Key words: local periodontitis, complex management of the local periodontitis.
Литература:
1. Антонова И.Н. Роль профессиональной гигиены полости рта в комплексном подходе к диагностике и лечению воспалительных заболеваний пародонта: Автореф. дисс. … к.м.н. - СПб., - 2000. - 17 с.
2. Васильев В.Г. Влияние препарирования зубов на ткани пародонта и сроки ортопедического лечения: Автореф. дисс. … д-ра мед. наук. - СПб, 1992. - 32 с.
3. Грудянов А.И., Овчинникова В.В. Профилактика воспалительных заболеваний пародонта. - М., ООО “МИА ”, 2007. - 80 с.
4. Иванов В.С. Заболевания пародонта / В.С.Иванов - М.: Медицина, 1998. - 295 с.
5. Лазерная допплеровская флоуметрия микроциркуляции крови / Под ред. А.И.Крупаткина, В.В.Сидорова: Руководство для врачей. - М.: ОАО “Издательство “Медицина”, 2005. - 256 с.
6. Логинова Н.К. Функциональная диагностика гипофункции жевательного аппарата и способы гнатотренинга // Институт Стоматологии. - 2004 - 4(25). - С. 46-48.
Ключевые слова: локализованный пародонтит, комплексное лечение пародонтита.
Сomplex management of local periodontitis of traumatic origin (A.V.Smirnova, B.T.Moroz).
Summary. Problems with restaurations, nonanatomical dental crowns without proximal points and harmful habits are counted the main causes of local periodontitis of traumatic origin. The prosthodontic methods are the most important part in multiple treatment of local periodontitis. The complex management of local periodontitis of traumatic origin is based on stopping of traumatic factor and defence of periodontal pocket for the subsequent regeneration.
Key words: local periodontitis, complex management of the local periodontitis.
Литература:
1. Антонова И.Н. Роль профессиональной гигиены полости рта в комплексном подходе к диагностике и лечению воспалительных заболеваний пародонта: Автореф. дисс. … к.м.н. - СПб., - 2000. - 17 с.
2. Васильев В.Г. Влияние препарирования зубов на ткани пародонта и сроки ортопедического лечения: Автореф. дисс. … д-ра мед. наук. - СПб, 1992. - 32 с.
3. Грудянов А.И., Овчинникова В.В. Профилактика воспалительных заболеваний пародонта. - М., ООО “МИА ”, 2007. - 80 с.
4. Иванов В.С. Заболевания пародонта / В.С.Иванов - М.: Медицина, 1998. - 295 с.
5. Лазерная допплеровская флоуметрия микроциркуляции крови / Под ред. А.И.Крупаткина, В.В.Сидорова: Руководство для врачей. - М.: ОАО “Издательство “Медицина”, 2005. - 256 с.
6. Логинова Н.К. Функциональная диагностика гипофункции жевательного аппарата и способы гнатотренинга // Институт Стоматологии. - 2004 - 4(25). - С. 46-48.
| Авторы: | Смирнова А.В., Мороз Б.Т. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 70 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В представленной работе была предпринята попытка проанализировать характер влияния ополаскивателей, содержащих активный аминофторид, на свойства ротовой жидкости лиц, подвергшихся воздействию электромагнитного излучения от персонального компьютера. Исследование включало в себя две серии наблюдений. Целью первой серии было оценить характер воздействия электромагнитного излучения компьютера на процесс кристаллизации ротовой жидкости человека, во второй — оценивался характер воздействия ополаскивателя на ротовую жидкость лиц, подвергшихся воздействию электромагнитного излучения компьютера. В конце исследований результаты обеих серий сравнивались. Экспериментальные данные показывают, что восстановление структуры минеральной составляющей ротовой жидкости после воздействия электромагнитного излучения от ПК в естественных условиях занимает продолжительный период времени, использование ополаскивателей с активным аминофторидом способствует ускорению данного процесса.
Ключевые слова: электромагнитное излучение, ротовая жидкость, микрокристаллизация, аминофторид.
Summary. In the present work an attempt has been made to analyze the impact of active aminfluoride containing rinses on the oral cavity liquid characteristics of the people being affected by personal computer electromagnetic emanation. The research contained two series of monitoring. The purpose of the first series was to evaluate the impact of the personal computer electromagnetic emanation on the process of the human oral cavity liquid crystallization. The purpose of the second series was to evaluate the impact of rinse on the oral cavity liquid of the people being affected by personal computer electro-magnetic emanation. In the end of the research the results of the both series were compared.
The experimental data show that restoration of the oral cavity liquid mineral structure after the impact of personal computer electro-magnetic emanation in a natural environment takes a substantial period of time. The use of active aminfluoride containing rinse favors the process to be more rapid.
Key words: electro-magnetic emanation, oral cavity liquid, micro-crystallization, aminfluoride.
Литература:
1. Борисенко М.А., Питаева А.И., Седельников В.В.,Ломиашвили Л.М. Влияние электромагнитного излученияПЭВМ на состав и структуру ротовой жидкости кариесрезистентных лиц // Институт стоматологии. - 2005. - №1. - С. 101-102.
2. Кучма В.Р. Гигиена детей и подростков при работе скомпьютерными видеодисплейными терминалами. - Москва: “Медицина”, 2000.
3. Ломиашвили Л.М., Борисенко М.А. Клинико-лабораторная характеристика органов и тканей полости рта лиц, работающих под воздействием электромагнитного излучения // Институт стоматологии. - 2007. - №1. - С. 76.
4. Леонтьев В.К. Кариес и процессы минерализации: дис. … д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1978. - 541 с.
5. Леонтьев В.К., Галиулина М.В. О мицеллярном состоянии слюны // Стоматология. - 1991. - №5. - С. 17-20.
6. Леус П.А. Клинико-экспериментальное исследованиепатогенеза, патогенетической консервативной терапии ипрофилактики кариеса зубов: автореф. дис. …д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1977. - 30 с.
7. Павленко А.Р. Компьютер, TV и здоровье. - Киев: “Основа”, 2002.
8. Ларс Г. Петерсон. Реминерализация очагов первичногокариеса корней зубов при использовании средств гигиеныполости рта с аминофторидом // Маэстро стоматологии. - 2009. - №1.
9. Саратовкин Д.Д. Дендритная кристаллизация. - Москва: “Металлургиздат”, 1957.
10. Федоров Ю.А., Дрожжина В.А. Клиника, диагностика и лечение некариозных поражений зубов // Новое в стоматологии. - 1997. - спецвыпуск.
Ключевые слова: электромагнитное излучение, ротовая жидкость, микрокристаллизация, аминофторид.
Summary. In the present work an attempt has been made to analyze the impact of active aminfluoride containing rinses on the oral cavity liquid characteristics of the people being affected by personal computer electromagnetic emanation. The research contained two series of monitoring. The purpose of the first series was to evaluate the impact of the personal computer electromagnetic emanation on the process of the human oral cavity liquid crystallization. The purpose of the second series was to evaluate the impact of rinse on the oral cavity liquid of the people being affected by personal computer electro-magnetic emanation. In the end of the research the results of the both series were compared.
The experimental data show that restoration of the oral cavity liquid mineral structure after the impact of personal computer electro-magnetic emanation in a natural environment takes a substantial period of time. The use of active aminfluoride containing rinse favors the process to be more rapid.
Key words: electro-magnetic emanation, oral cavity liquid, micro-crystallization, aminfluoride.
Литература:
1. Борисенко М.А., Питаева А.И., Седельников В.В.,Ломиашвили Л.М. Влияние электромагнитного излученияПЭВМ на состав и структуру ротовой жидкости кариесрезистентных лиц // Институт стоматологии. - 2005. - №1. - С. 101-102.
2. Кучма В.Р. Гигиена детей и подростков при работе скомпьютерными видеодисплейными терминалами. - Москва: “Медицина”, 2000.
3. Ломиашвили Л.М., Борисенко М.А. Клинико-лабораторная характеристика органов и тканей полости рта лиц, работающих под воздействием электромагнитного излучения // Институт стоматологии. - 2007. - №1. - С. 76.
4. Леонтьев В.К. Кариес и процессы минерализации: дис. … д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1978. - 541 с.
5. Леонтьев В.К., Галиулина М.В. О мицеллярном состоянии слюны // Стоматология. - 1991. - №5. - С. 17-20.
6. Леус П.А. Клинико-экспериментальное исследованиепатогенеза, патогенетической консервативной терапии ипрофилактики кариеса зубов: автореф. дис. …д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1977. - 30 с.
7. Павленко А.Р. Компьютер, TV и здоровье. - Киев: “Основа”, 2002.
8. Ларс Г. Петерсон. Реминерализация очагов первичногокариеса корней зубов при использовании средств гигиеныполости рта с аминофторидом // Маэстро стоматологии. - 2009. - №1.
9. Саратовкин Д.Д. Дендритная кристаллизация. - Москва: “Металлургиздат”, 1957.
10. Федоров Ю.А., Дрожжина В.А. Клиника, диагностика и лечение некариозных поражений зубов // Новое в стоматологии. - 1997. - спецвыпуск.
| Авторы: | Ломиашвили Л.М., Седельников В.В., Борисенко М.А., Елендо М.Б. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 68-69 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В данной статье описывается запатентованный атравматический способ реставрации режущего края поврежденного зуба глубиной до 2 мм с применением композитных материалов, который позволяет восстановить целостность режущего края прямым способом. Реставрация режущего края проводится с учетом анатомо-топографических и биомеханических особенностей строения коронковой части зуба. Формирование шероховатости, ретенционных пунктов и ретенционной полости со сложной геометрической конфигурацией обеспечивают ретенцию композитного материала с твердыми тканями зуба и увеличивают долговечность реставрации.
Ключевые слова: дефект режущего края, атравматическое одонтопрепарирование, минимальная инвазивная стоматология, ретенционный пункт, продольный паз, ретенционная полость, искусственная эмаль, искусственный дентин, композитный валик, коронковая часть зуба, композит, композитная реставрация.
The atraumatic technique of restoration/reconstruction of incisal edge of the defective tooth depth 2 mm using a composite materials.
Summary.This article is describe the atraumatic patented technique of restoration of incisal edge with 2 mm defect using a composite which allows to restore integrity of incisal edge in the direct way. The incisal edge is restore with the account of anatomico-topographic and biomechanical features of tooth crown. The roughness formation, retentional points and retentional cavities with a difficult geometrical configuration provide retention of composite material with hard tooth tissues and increase the durability of restoration.
Key words: Incisal edge, atraumatic tooth preparation, minimally invasive dentistry, retentional points, longitudinal chamfer, retentional cavity, artificial dentine, artificial enamel, composite roller, coronal tooth structure, composite, composite restoration.
Литература:
1. Боровский Е.В. Терапевтическая стоматология // Медицина. Москва. - 1997. - С. 163-167.
2. Макеева И.М. Поражения твердых тканей зуба по типу VI класса // Клиническая стоматология. - 2001. - №3. - С. 59-59.
3. Каламкаров Х.А. Ортопедическое лечение с применением металлокерамических протезов // Москва. Медицинское информационное агентство. - 2003. - С. 57 - 61.
4. Копейкин В.Н. Руководство по ортопедической стоматологии // Москва. Медицина. - 1993. - С. 121-123.
5. Куцын С.Н. Клиническое использование современных материалов фирмы VOCO // Стоматология. - 2006. - №1. - С. 58-59.
6. Суржанский Ю.Н. Реставрационные материалы и основы практической эндодонтии// Киев. Книга плюс. - 2004. - С. 70-72.
7. Борисенко А.В. Секреты лечения кариеса и реставрации зубов // Киев. Книга плюс. - 2002. - С. 363-365.
8. Луцкая И.К. Основы эстетической стоматологии // Минск. Современная школа. - 2005. - С. 290-291.
9. Борисенко А.В. Композиционные пломбировочные и облицовочные материалы в стоматологии // Киев. Книга плюс. - 2001. - С. 200.
10. Николаев А.И. Практическая терапевтическая стоматология. Санкт-Петербургский институт стоматологии. Санкт-Петербург. - 2001. - С. 91-100.
11. Петрович В.Н. Применение парапульпарных штифтов в полостях в II класса по Блэку в эксперименте // Сборник “Организация и профилактика в стоматологии”. Екатеринбург. - 1993. - С. 105-110.
12. Меликян М.Л. Применение пористой проницаемой титановой пластинки при реставрации режущего края зуба // Патент RU. №2214194. Приоритет от 08.01.2002.
13. Меликян М.Л., Меликян Г.М., Способ реставрации режущего края поврежденного зуба // Патент RU. №2214195. Приоритет от 08.01.2002.
14. Меликян М.Л., Меликян Г.М., Меликян.К.М., Давыдова К.И. Способ устранения дефекта режущего края глубиной до 2 мм с применением композитных материалов // Патент RU №2331385. Приоритет от 01.02.2007.
Ключевые слова: дефект режущего края, атравматическое одонтопрепарирование, минимальная инвазивная стоматология, ретенционный пункт, продольный паз, ретенционная полость, искусственная эмаль, искусственный дентин, композитный валик, коронковая часть зуба, композит, композитная реставрация.
The atraumatic technique of restoration/reconstruction of incisal edge of the defective tooth depth 2 mm using a composite materials.
Summary.This article is describe the atraumatic patented technique of restoration of incisal edge with 2 mm defect using a composite which allows to restore integrity of incisal edge in the direct way. The incisal edge is restore with the account of anatomico-topographic and biomechanical features of tooth crown. The roughness formation, retentional points and retentional cavities with a difficult geometrical configuration provide retention of composite material with hard tooth tissues and increase the durability of restoration.
Key words: Incisal edge, atraumatic tooth preparation, minimally invasive dentistry, retentional points, longitudinal chamfer, retentional cavity, artificial dentine, artificial enamel, composite roller, coronal tooth structure, composite, composite restoration.
Литература:
1. Боровский Е.В. Терапевтическая стоматология // Медицина. Москва. - 1997. - С. 163-167.
2. Макеева И.М. Поражения твердых тканей зуба по типу VI класса // Клиническая стоматология. - 2001. - №3. - С. 59-59.
3. Каламкаров Х.А. Ортопедическое лечение с применением металлокерамических протезов // Москва. Медицинское информационное агентство. - 2003. - С. 57 - 61.
4. Копейкин В.Н. Руководство по ортопедической стоматологии // Москва. Медицина. - 1993. - С. 121-123.
5. Куцын С.Н. Клиническое использование современных материалов фирмы VOCO // Стоматология. - 2006. - №1. - С. 58-59.
6. Суржанский Ю.Н. Реставрационные материалы и основы практической эндодонтии// Киев. Книга плюс. - 2004. - С. 70-72.
7. Борисенко А.В. Секреты лечения кариеса и реставрации зубов // Киев. Книга плюс. - 2002. - С. 363-365.
8. Луцкая И.К. Основы эстетической стоматологии // Минск. Современная школа. - 2005. - С. 290-291.
9. Борисенко А.В. Композиционные пломбировочные и облицовочные материалы в стоматологии // Киев. Книга плюс. - 2001. - С. 200.
10. Николаев А.И. Практическая терапевтическая стоматология. Санкт-Петербургский институт стоматологии. Санкт-Петербург. - 2001. - С. 91-100.
11. Петрович В.Н. Применение парапульпарных штифтов в полостях в II класса по Блэку в эксперименте // Сборник “Организация и профилактика в стоматологии”. Екатеринбург. - 1993. - С. 105-110.
12. Меликян М.Л. Применение пористой проницаемой титановой пластинки при реставрации режущего края зуба // Патент RU. №2214194. Приоритет от 08.01.2002.
13. Меликян М.Л., Меликян Г.М., Способ реставрации режущего края поврежденного зуба // Патент RU. №2214195. Приоритет от 08.01.2002.
14. Меликян М.Л., Меликян Г.М., Меликян.К.М., Давыдова К.И. Способ устранения дефекта режущего края глубиной до 2 мм с применением композитных материалов // Патент RU №2331385. Приоритет от 01.02.2007.
| Авторы: | Меликян М.Л., Меликян Г.М., Меликян К.М., Давыдова К.И. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 64-67 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Изучались клинические возможности нового нанокомпозита Brilliant New Line производства Coltene/Whaledent при лечении дисколоритов твердых тканей зуба различной этиологии методом прямой анатомической реставрации с предварительной оценкой цвета в системе L*a*b. Применение специальных оттенков Super White и Transparent для воссоздания характеризации эмали значительно повышает эстетическую эффективность реставрации.
Ключевые слова: дисколорит, нанокомпозит, анатомическая реставрация, характеризация.
The use of expanded set of nanocomposite Brilliant New Line manufactured by Coltene/Whaledent in treatment of discolour of tooth hard tissues of different origin (B.R. Shumilovich, MD, PhD, Assistant professor to chair of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, Doctor of the highest category; D.A. Kunin, resident of the department of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, applicant; L.V. Bessonova, resident of the department of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, applicant).
Summary. Clinical possibilities of new nanocomposite Brilliant New Line manufactured by Coltene/Whaledent were studied in treatment of discolour of tooth hard tissues of different origin by means of direct anatomy restoration and preliminary estimation of colour in L*a*b system. The use of special composite shadow Super White and Transparent notably increases esthetic efficiency of the restoration.
Key words: discolour, nanocomposite, anatomy restoration, characterization.
ЛИТЕРАТУРА:
1. Бойко В.В. Как показать “невидимое” качество лечения в процессе его осуществления / В.В.Бойко, А.В.Долгих // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - Т. 37, № 4. - С. 10-15.
2. Зойбельманн М. Практическое значение управления качеством в зубоврачебной клинике / М.Зойбельманн, П.Парвини // Сб. материалов международ. конф. по итогам выполнения программы “Tempus - Tacis” и науч. сессии каф. терапевт. стоматологии “Qualitatsmanagement в стоматологии”. - Воронеж, 2005. - С. 90-97.
3. Кунин А.А. Выделение информативных показателей эстетической реставрации методом априорного ранжирования / А.А.Кунин, О.И.Олейник, И.Н.Сарычева // Сб. науч. и практ. работ конф., посвящ. 30-летию МУЗ “Гор. больница № 1”, г.Ст.Оскол. - Ст.Оскол : Истоки, 2005. - С. 192-195.
4. Кунин А.А. Клинические возможности нанокомпозита Brilliant New Line производства Coltene/ Whaledent при прямых реставрациях различных групп зубов / А.А.Кунин, Б.Р.Шумилович, А.В.Потапов // Институт стоматологии. - 2009. - №.. - С.
5. Кунин А.А. Применение Fine Hybrid композита MIRIS производства Coltene/Whaledent при прямых реставрациях с повышенными требованиями к эстетике / А.А.Кунин, Б.Р.Шумилович, А.В.Потапов // Новое в стоматологии. - 2010. - №.. - С.
6. Леонтьев В.К. О состоянии стоматологии в России и перспективах ее развития (Часть I) / В.К.Леонтьев // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №4(33). - С. 10-13.
7. Леонтьев В.К. О состоянии стоматологии в России и перспективах ее развития (Часть II) / В.К.Леонтьев, В.В.Садовский, В.М.Гринин, А.В.Федоров, Д.А.Петраш // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №4(33). - С. 10-13.
8. Сарычева И.Н. Изменение цветовых параметров и микрохимического состава твердых тканей в различных анатомических зонах зуба: Дис. … канд. мед. наук / И.Н.Сарычева. - Воронеж, 2006. - 169 с.
9. Хельвиг Э., Климек Й. Аттин Т. Терапевтическая стоматология. (Под ред. проф. А.М.Политун, проф. Н.И.Смоляр. Пер. с нем. - Львов; Гал Dent. 1999. - 409 c.
10. Шмидседер Д. Эстетическая стоматология: пер. с англ. / Д.Шмидседер; под ред. Т.Ф.Виноградовой. - М. : Медпресс-информ, 2004. - 314 с.
11. Cook W.D. Optical properties of esthetic restorative materials and natural dentition / W.D.Cook, D.C.McAree // J. Biomat. Mat. Res. - 1985. - Vol. 19. - P. 469-488.
12. Dietschi D. Free-hand composite resin restorations: a key to anterior aesthetics / D.Dietschi // Pract. Periodontal & Aesthetic Dent. - 1995. - Vol. 7. - P. 15-25.
13. Dietschi D. Free-hand bonding in esthetic treatment of anterior teeth: creating the illusion / D.Dietschi // J. Esthet. Dent. - 1997. - Vol. 9. - P. 156-164.
14. Dietschi D. Exploring the layering concepts for anterior teeth. In Roulet J.F. and Degrange M., Editors: Adhesion - The silent revolution in Dentistry / D.Dietschi, S.Ardu, I.Kreiji // Berlin. Quintessense Publishing. - 2000. - P. 235-251.
Ключевые слова: дисколорит, нанокомпозит, анатомическая реставрация, характеризация.
The use of expanded set of nanocomposite Brilliant New Line manufactured by Coltene/Whaledent in treatment of discolour of tooth hard tissues of different origin (B.R. Shumilovich, MD, PhD, Assistant professor to chair of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, Doctor of the highest category; D.A. Kunin, resident of the department of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, applicant; L.V. Bessonova, resident of the department of therapeutic dentistry, Burdenko VGMA, applicant).
Summary. Clinical possibilities of new nanocomposite Brilliant New Line manufactured by Coltene/Whaledent were studied in treatment of discolour of tooth hard tissues of different origin by means of direct anatomy restoration and preliminary estimation of colour in L*a*b system. The use of special composite shadow Super White and Transparent notably increases esthetic efficiency of the restoration.
Key words: discolour, nanocomposite, anatomy restoration, characterization.
ЛИТЕРАТУРА:
1. Бойко В.В. Как показать “невидимое” качество лечения в процессе его осуществления / В.В.Бойко, А.В.Долгих // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - Т. 37, № 4. - С. 10-15.
2. Зойбельманн М. Практическое значение управления качеством в зубоврачебной клинике / М.Зойбельманн, П.Парвини // Сб. материалов международ. конф. по итогам выполнения программы “Tempus - Tacis” и науч. сессии каф. терапевт. стоматологии “Qualitatsmanagement в стоматологии”. - Воронеж, 2005. - С. 90-97.
3. Кунин А.А. Выделение информативных показателей эстетической реставрации методом априорного ранжирования / А.А.Кунин, О.И.Олейник, И.Н.Сарычева // Сб. науч. и практ. работ конф., посвящ. 30-летию МУЗ “Гор. больница № 1”, г.Ст.Оскол. - Ст.Оскол : Истоки, 2005. - С. 192-195.
4. Кунин А.А. Клинические возможности нанокомпозита Brilliant New Line производства Coltene/ Whaledent при прямых реставрациях различных групп зубов / А.А.Кунин, Б.Р.Шумилович, А.В.Потапов // Институт стоматологии. - 2009. - №.. - С.
5. Кунин А.А. Применение Fine Hybrid композита MIRIS производства Coltene/Whaledent при прямых реставрациях с повышенными требованиями к эстетике / А.А.Кунин, Б.Р.Шумилович, А.В.Потапов // Новое в стоматологии. - 2010. - №.. - С.
6. Леонтьев В.К. О состоянии стоматологии в России и перспективах ее развития (Часть I) / В.К.Леонтьев // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №4(33). - С. 10-13.
7. Леонтьев В.К. О состоянии стоматологии в России и перспективах ее развития (Часть II) / В.К.Леонтьев, В.В.Садовский, В.М.Гринин, А.В.Федоров, Д.А.Петраш // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №4(33). - С. 10-13.
8. Сарычева И.Н. Изменение цветовых параметров и микрохимического состава твердых тканей в различных анатомических зонах зуба: Дис. … канд. мед. наук / И.Н.Сарычева. - Воронеж, 2006. - 169 с.
9. Хельвиг Э., Климек Й. Аттин Т. Терапевтическая стоматология. (Под ред. проф. А.М.Политун, проф. Н.И.Смоляр. Пер. с нем. - Львов; Гал Dent. 1999. - 409 c.
10. Шмидседер Д. Эстетическая стоматология: пер. с англ. / Д.Шмидседер; под ред. Т.Ф.Виноградовой. - М. : Медпресс-информ, 2004. - 314 с.
11. Cook W.D. Optical properties of esthetic restorative materials and natural dentition / W.D.Cook, D.C.McAree // J. Biomat. Mat. Res. - 1985. - Vol. 19. - P. 469-488.
12. Dietschi D. Free-hand composite resin restorations: a key to anterior aesthetics / D.Dietschi // Pract. Periodontal & Aesthetic Dent. - 1995. - Vol. 7. - P. 15-25.
13. Dietschi D. Free-hand bonding in esthetic treatment of anterior teeth: creating the illusion / D.Dietschi // J. Esthet. Dent. - 1997. - Vol. 9. - P. 156-164.
14. Dietschi D. Exploring the layering concepts for anterior teeth. In Roulet J.F. and Degrange M., Editors: Adhesion - The silent revolution in Dentistry / D.Dietschi, S.Ardu, I.Kreiji // Berlin. Quintessense Publishing. - 2000. - P. 235-251.
| Авторы: | Шумилович Б.Р., Потапов А.В., Бессонова Л.В. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 60-63 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. При лечении аномалий прикуса с использованием несъемной ортодонтической аппаратуры ухудшаются условия для проведения гигиены полости рта, врезультате чего увеличивается прирост кариеса зубов. Впроцессе ортодонтического лечения определение участков деминерализации доступными методами составляет определенные сложности, они чаще всего выявляются в виде “белых” пятен только на этапе снятия ортодонтической аппаратуры. В ходе исследования нами применялся метод лазерной флюоресцентной спектроскопии. Проанализировав данные, можно говорить, чтовысокий уровень риска развития кариеса зубов через месяц после наклейки бреккет-системы отмечается в пришеечной области центральных и латеральных резцов верхней челюсти, клыков верхней и нижней челюстей, премоляров верхней челюсти, первых моляров нижней челюсти, вторых моляров верхней и нижнейчелюстей, в фиссурах первых премоляров верхней инижней челюстей, вторых премоляров верхней челюсти, вторых молярах нижней и верхней челюстей. Средний уровень риска развития кариеса — в пришеечной области первых моляров верхней челюсти, центральныхи латеральных резцов, первых и вторых премоляров нижней челюсти, в области фиссур первых и вторых моляров верхней челюсти, первых премоляров и моляров нижней челюсти, а также на аппроксимальных поверхностях всех зубов.
Ключевые слова: кариес, лазерная флюоресцентная спектроскопия,ортодонтическое лечение на несъемной аппаратуре.
Evaluation of dental tissues by laser fluorescence spectroscopy in patients 16-18 years in preparation for orthodontic treatment (Satygo E.A, Bryantseva E.S.).
Resume. In the treatment of bite anomalies on fixed orthodontic equipment deteriorating conditions for oral hygiene, resulting in increased growth of dental caries. In the process of orthodontic treatment definition sites demineralization available methods of some complexity and often revealed in the form of “white” spots only at the stage of removal of orthodontic equipment. During research we applied a method of laser fluorescent spectroscopy .After analyzing the data we can say that the high risk of developing dental caries over a month after the stickers brackets system noted in the cervical area of central and lateral incisors of the upper jaw, the canines of the upper and lower jaw, upper jaw premolars, first molars of the mandible, the second molars of the upper and lower jaw. At the fissure first premolars upper and lower jaw second premolars of the upper jaw, the second molars of the lower and upper jaw. The average risk of developing caries in the cervical area of the first molars of the upper jaw, central and lateral incisors, first and second premolars of the mandible in the fissures of first and second molars of the upper jaw, the first premolars and molars of the mandible. And as to the aproximal surfaces of all teeth.
Key words: caries, laser fluorescence spectroscopy, orthodontic treatment.
Литература:
1. Аксамит Л.А. Диагностика начальной деминерализации эмали методом окрашивания / Результаты клинических и экспериментальных исследований/. - М., 1973. - С. 4-5.
2. Михайлова Е.С. Состояние гемодинамики тканей пародонта в процессе комплексного лечения аномалий положения зубов: Автореф. дис. ... канд. мед. наук. - СПб. - 2000.
3. Петрова Н.П. Изучение микрофлоры и некоторых биохимических показателей ротовой жидкости у детей и подростков, пользующихся съемными и несъемными ортодонтическими аппаратами/ Н.П.Петрова, Б.Т.Мороз, Н.М.Медведовская, М.С.Жуманкулов, Д.Ю.Березин // Диагностика и комлексное лечение при зубочелюстно-лицевых аномалиях, сочетающихся е врожденным несращением верхней губы, альвеолярного отростка, неба. / Под редакцией Хорошилкиной Ф.Я. - СПб., 2001. - С. 228-237.
4. Электрометрическая диагностика начального, фиссурного, рецидивного кариеса и других поражений твердых тканей зубов с законченной минерализацией эмали / В.К.Леонтьев, Г.Г.Иванова, Т.Н.Жорова / Методические рекомендации, Минздрав РСФСР, Омск, 1988.
5. Lussi A.P. Francescut. Perfomanceofconveationl and new metod for the detection of occlusal caries in deciduous teeth.Caries, 2003, 37(1): 2-7.
6. Francescut P.Lussi A.Correlationbetween fissure discoloration.diagnodent measurement? and caries depth an in vitro study.Pediatr Dent, 2003, 25(6): 559-64.
Ключевые слова: кариес, лазерная флюоресцентная спектроскопия,ортодонтическое лечение на несъемной аппаратуре.
Evaluation of dental tissues by laser fluorescence spectroscopy in patients 16-18 years in preparation for orthodontic treatment (Satygo E.A, Bryantseva E.S.).
Resume. In the treatment of bite anomalies on fixed orthodontic equipment deteriorating conditions for oral hygiene, resulting in increased growth of dental caries. In the process of orthodontic treatment definition sites demineralization available methods of some complexity and often revealed in the form of “white” spots only at the stage of removal of orthodontic equipment. During research we applied a method of laser fluorescent spectroscopy .After analyzing the data we can say that the high risk of developing dental caries over a month after the stickers brackets system noted in the cervical area of central and lateral incisors of the upper jaw, the canines of the upper and lower jaw, upper jaw premolars, first molars of the mandible, the second molars of the upper and lower jaw. At the fissure first premolars upper and lower jaw second premolars of the upper jaw, the second molars of the lower and upper jaw. The average risk of developing caries in the cervical area of the first molars of the upper jaw, central and lateral incisors, first and second premolars of the mandible in the fissures of first and second molars of the upper jaw, the first premolars and molars of the mandible. And as to the aproximal surfaces of all teeth.
Key words: caries, laser fluorescence spectroscopy, orthodontic treatment.
Литература:
1. Аксамит Л.А. Диагностика начальной деминерализации эмали методом окрашивания / Результаты клинических и экспериментальных исследований/. - М., 1973. - С. 4-5.
2. Михайлова Е.С. Состояние гемодинамики тканей пародонта в процессе комплексного лечения аномалий положения зубов: Автореф. дис. ... канд. мед. наук. - СПб. - 2000.
3. Петрова Н.П. Изучение микрофлоры и некоторых биохимических показателей ротовой жидкости у детей и подростков, пользующихся съемными и несъемными ортодонтическими аппаратами/ Н.П.Петрова, Б.Т.Мороз, Н.М.Медведовская, М.С.Жуманкулов, Д.Ю.Березин // Диагностика и комлексное лечение при зубочелюстно-лицевых аномалиях, сочетающихся е врожденным несращением верхней губы, альвеолярного отростка, неба. / Под редакцией Хорошилкиной Ф.Я. - СПб., 2001. - С. 228-237.
4. Электрометрическая диагностика начального, фиссурного, рецидивного кариеса и других поражений твердых тканей зубов с законченной минерализацией эмали / В.К.Леонтьев, Г.Г.Иванова, Т.Н.Жорова / Методические рекомендации, Минздрав РСФСР, Омск, 1988.
5. Lussi A.P. Francescut. Perfomanceofconveationl and new metod for the detection of occlusal caries in deciduous teeth.Caries, 2003, 37(1): 2-7.
6. Francescut P.Lussi A.Correlationbetween fissure discoloration.diagnodent measurement? and caries depth an in vitro study.Pediatr Dent, 2003, 25(6): 559-64.
| Авторы: | Сатыго Е.А., Брянцева Е.С. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 58-59 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В настоящей работе представлены результаты собственных исследований. Выявлена противомикробная активность препарата “Стоматофит А”. Изучена клиническая эффективность локального применения препаратов “Стоматофит” и “Стоматофит А” в комплексном лечении 20 пациентов с различными заболеваниями слизистой оболочки рта. Анализ проведённых исследований свидетельствует о наличии у препарата “Стоматофит А” противомикробной активности в отношении ряда условно-патогенных микроорганизмов. Препараты “Стоматофит” и “Стоматофит А” показали высокую клиническую эффективность при местном лечении заболеваний слизистой оболочки рта.
Ключевые слова: “Стоматофит”, “Стоматофит А”, лечение заболеваний слизистой оболочки рта.
Clinical and laboratory substantiation of application of vegetative preparations “Stomatofit” and “Stomatofit A” in complex treatment of oral mucosa diseases (I.V.Anisimova — к.м.s., the assistant to chair of therapeutic stomatology, Omsk state medical academy; M.O.Nagaeva — к.м.s., the assistant to chair of therapeutic stomatology, Omsk state medical academy).
Summary. In this article are presented the results of the own research. The antimicrobial activity of the drug “Stomatofit А” was studied. The clinical effectiveness of local applications “Stomatofita” and “Stomatofita A “ was also studied in the comprehensive treatment of 20 patients with various diseases of the oral mucosa.
Analysis of indicated studies shows the presence in a drug “Stomatofit A” on antimicrobial activity against a number of opportunistic microorganisms. The preparations “Stomatofit” and “Stomatofit A” demonstrated high clinical effect of the use in the local treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa.
Key words: “Stomatofit”, “Stomatofit A”, treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa.
Литература:
1. Анисимова И.В. Клиника, диагностика и лечение заболеваний слизистой оболочки полости рта /И.В.Анисимова, В.Б.Недосеко, Л.М.Ломиашвили. - М.: Медицинская книга, 2008. - 194 с.
2. Каргальцева Н.М. Ротовая полость - важный биотоп организма человека. /Н.М. Каргальцева // Институт Стоматологии. - 2001. - №1 (10). - С.18-21.
3. Леонтьев В.К. Профилактика стоматологических заболеваний. / В.К.Леонтьев, Г.Н.Пахомов. - М.: 2006. - 416 с.
4. Максимовский Ю.М. Препарат “Стоматофит” в комплексном лечении воспалительных заболеваний пародонта. / Ю.М.Максимовский., Т.Д.Чиркова, М.А.Ульянова //Пародонтология. - 2008. - №4 (49). - С.3-6.
Ключевые слова: “Стоматофит”, “Стоматофит А”, лечение заболеваний слизистой оболочки рта.
Clinical and laboratory substantiation of application of vegetative preparations “Stomatofit” and “Stomatofit A” in complex treatment of oral mucosa diseases (I.V.Anisimova — к.м.s., the assistant to chair of therapeutic stomatology, Omsk state medical academy; M.O.Nagaeva — к.м.s., the assistant to chair of therapeutic stomatology, Omsk state medical academy).
Summary. In this article are presented the results of the own research. The antimicrobial activity of the drug “Stomatofit А” was studied. The clinical effectiveness of local applications “Stomatofita” and “Stomatofita A “ was also studied in the comprehensive treatment of 20 patients with various diseases of the oral mucosa.
Analysis of indicated studies shows the presence in a drug “Stomatofit A” on antimicrobial activity against a number of opportunistic microorganisms. The preparations “Stomatofit” and “Stomatofit A” demonstrated high clinical effect of the use in the local treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa.
Key words: “Stomatofit”, “Stomatofit A”, treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa.
Литература:
1. Анисимова И.В. Клиника, диагностика и лечение заболеваний слизистой оболочки полости рта /И.В.Анисимова, В.Б.Недосеко, Л.М.Ломиашвили. - М.: Медицинская книга, 2008. - 194 с.
2. Каргальцева Н.М. Ротовая полость - важный биотоп организма человека. /Н.М. Каргальцева // Институт Стоматологии. - 2001. - №1 (10). - С.18-21.
3. Леонтьев В.К. Профилактика стоматологических заболеваний. / В.К.Леонтьев, Г.Н.Пахомов. - М.: 2006. - 416 с.
4. Максимовский Ю.М. Препарат “Стоматофит” в комплексном лечении воспалительных заболеваний пародонта. / Ю.М.Максимовский., Т.Д.Чиркова, М.А.Ульянова //Пародонтология. - 2008. - №4 (49). - С.3-6.
| Авторы: | Анисимова И.В., Нагаева М.О. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 55-57 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В статье приведен краткий обзор литературных данных о применении препаратов протеолитических ферментов в челюстно-лицевой хирургии и стоматологии. Сочетание нескольких позитивных клинико-лабораторных эффектов делают применение современных пероральных энзимных препаратов патогенетически обоснованным методом лечения в стоматологии.
Ключевые слова: энзимы, протеиназы, антибактериальная терапия, гнойно-воспалительные заболевания.
Proteolytic enzyme therapy in dentistrySummary. Brief literature review regarding clinical efficacy of Systemic enzyme therapy in maxillo-facial surgery and in dentistry are presented in this article. Due to the combination of it’s various positive clinical & laboratory effects, modern peroral enzymic preparations are pathogenic feasible treatment method in Dentistry.
Key words: enzymes, proteinases, antibiotic treatment, pyoinflammatory.
Литература:
1. Алпатова В.Г., Скрыль А.В. Применение иммобилизованных бактериальных протеиназ в клинике терапевтической стоматологии для лечения кариеса и егоосложнений // Актуальные проблемы теории и практики в стоматологии. - Ставрополь, 1998. - С. 104-105.
2. Ануфриева О.И., Железный П.А., Цирельников Н.И. Клинико-морфологические особенности хронического периодонтита постоянных зубов у детей при лечении иммобилизованными протеолитическими ферментами. // Стоматология детского возраста и профилактика. - 2001. - №1.
3. Артеменко К.Л. Кнорринг Г.Ю. Опыт применения ферментного комплекса вобэнзим у больных с абсцессами и флегмонами челюстно-лицевой области // Ученые записки, т. ХII, №3. - 2005. - С. 43-47.
4. Балин В.Н., Прохватилов Г.И., Нефедов A.В. Основныеаспекты лечения гнойно-воспалительных заболеванийв условиях регулируемой активности раневых энзимов // Стоматология. - 1996., Спец. выпуск. - С. 17-19.
5. Бушковская А.С., Дрегалкина А.А., Васильева Е.С. Применение флогэнзима - препарата системной энзимотерапии в комплексном лечении флегмон челюстно-лицевой области // Урал. стоматол. журн. - 2002. - №2. - С. 37-39.
6. Горбачева И.А. Комплексные подходы к лечению больных с сочетанными заболеваниями внутренних органов и воспалительными поражениями пародонта: Автореф. дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - СПб, 2004. - 34 с.
7. Гостищев В.К. Энзимотерапия неспецифической хирургической инфекции: Автореф. … дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1972. - 34 с.
8. Ефименко Н.А., Новожилов А.А., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Системная энзимотерапия в гнойной хирургии // Амбулаторная хирургия. - 2005. - №3. - С. 51-55.
9. Заря О.И. Обоснование использования иммобилизированных протеолитических ферментов в лечебно-профилактических зубных пастах: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Омск, 1994. - 20 с.
10. Использование энзимных препаратов в хирургической стоматологии и челюстно-лицевой хирургии: Методические рекомендации. Сост.: Дрегалкина А.А., Васильева Е.С. - Екатеринбург: УГМА, 2003. - 25 с.
11. Корчак Л.Ф. Применение ферментов протеолиза в лечении одонтогенных воспалительных процессов челюстно-лицевой области: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Киев, 1972. - 30 с.
12. Котельников Г.П., Труханова И.Г., Труханов В.В. Возможности коррекции иммунных нарушений при челюстно-лицевой травме // Тез. докл. Всеросс. конф. с международным участием “Проблемы реабилитации в оториноларингологии”. - Самара, 2003. - С. 56-57.
13. Кошкин В.М., Минаев С.В., Спесивцев Ю.А., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Полиферментные препараты в хирургической практике. - СПб.: Человек, 2004. – 112 с.
14. Кузьмина Э.М., Иванов В.Н., Иванова Е.Н. и др. Ферменты в предупреждении кариеса зубов // Новое в стоматологии. - 1996. - № 1. - С. 34-36.
15. Любенко О.Г., Москвичев В.Е., Родин Р.Ю., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Системная энзимотерапия при острых состояниях в стоматологии // Стоматолог. - 2007. - №12. - С. 58-61.
16. Минаев С.В., Ибрагимов О.Р., Зеленский В.А., Минаева Н.В. Улучшение результатов лечения больных с гнойно-воспалительными заболеваниями в челюстно-лицевой хирургии // Военно-Медицинский журнал. - 2007. - №11. - С. 52-58.
17. Минаев С.В., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Технология системной энзимотерапии в хирургической практике // Амбулаторная хирургия. - 2007. - №2 (26). - С. 89-92.
18. Мнацакалян Э.А. Применение протеолитических ферментов в лечении острых гнойных периодонтитов и острых гнойных периоститов. // Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Ереван, 1971.
19. Непомнящая Н.В., Гильмияров Э.М., Постников М.А. Комплексное лечение хронического пародонтита у пациентов с зубочелюстными аномалиями в зависимости от групповой принадлежности крови. // Стоматологический Вестник Поволжья. - 2009. - №1 (16). - С. 8-10.
20. Притыко А.Г., Балакирева Г.М., Мкртумян Э.С. и др. Опыт применения препарата Вобэнзим при костной пластике врожденной расщелины альвеолярного отростка верхней челюсти у детей // J. of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. - 1998. Vol. 26 (Suppl. 1). №8. P. 106.
21. Притыко А.Г., Лопатин А.В., Гончаков Г.В. Применение Флогэнзима и Вобэнзима в клинике детской черепно-лицевой хирургии // Мат. науч.-практ. конф. “Новые аспекты системной энзимотерапии”. - М., 2001. - С. 147-151.
22. Прудникова О.В. Разработка и обоснование методовлечения хронического периодонтита с применением литического ферментного препарата лизоамидазы: Автореф. дис. ... канд. мед. наук. - М. - 1997.
23. Ремезов А.П., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Cистемная энзимотерапия как способ потенцирования антибактериальных средств // Антибиотики и химиотерапия. - 2003. - Т. 48. №3. - С. 30-33.
24. Abbott P.V., Hume W.R., Pearman J.W. Antibiotics and endodontics. Austral Dental J 1990; 35: 50-60.
25. Navrátilová B., Navrátil L. Use of systemic enzyme therapy in stomatology - current options (preliminary study). Miniinvazivní terapie - 1998, №3. - str. 106-109.
26. Vinzenz K. Edema therapy in dental interventions with hydrolytic enzymes. [Odembehandlung bei zahnchirurgischen Eingriffen mit hydrolytischen Enzymen] Quintessenz. 1991: 42 (7):1053-1064.
Ключевые слова: энзимы, протеиназы, антибактериальная терапия, гнойно-воспалительные заболевания.
Proteolytic enzyme therapy in dentistrySummary. Brief literature review regarding clinical efficacy of Systemic enzyme therapy in maxillo-facial surgery and in dentistry are presented in this article. Due to the combination of it’s various positive clinical & laboratory effects, modern peroral enzymic preparations are pathogenic feasible treatment method in Dentistry.
Key words: enzymes, proteinases, antibiotic treatment, pyoinflammatory.
Литература:
1. Алпатова В.Г., Скрыль А.В. Применение иммобилизованных бактериальных протеиназ в клинике терапевтической стоматологии для лечения кариеса и егоосложнений // Актуальные проблемы теории и практики в стоматологии. - Ставрополь, 1998. - С. 104-105.
2. Ануфриева О.И., Железный П.А., Цирельников Н.И. Клинико-морфологические особенности хронического периодонтита постоянных зубов у детей при лечении иммобилизованными протеолитическими ферментами. // Стоматология детского возраста и профилактика. - 2001. - №1.
3. Артеменко К.Л. Кнорринг Г.Ю. Опыт применения ферментного комплекса вобэнзим у больных с абсцессами и флегмонами челюстно-лицевой области // Ученые записки, т. ХII, №3. - 2005. - С. 43-47.
4. Балин В.Н., Прохватилов Г.И., Нефедов A.В. Основныеаспекты лечения гнойно-воспалительных заболеванийв условиях регулируемой активности раневых энзимов // Стоматология. - 1996., Спец. выпуск. - С. 17-19.
5. Бушковская А.С., Дрегалкина А.А., Васильева Е.С. Применение флогэнзима - препарата системной энзимотерапии в комплексном лечении флегмон челюстно-лицевой области // Урал. стоматол. журн. - 2002. - №2. - С. 37-39.
6. Горбачева И.А. Комплексные подходы к лечению больных с сочетанными заболеваниями внутренних органов и воспалительными поражениями пародонта: Автореф. дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - СПб, 2004. - 34 с.
7. Гостищев В.К. Энзимотерапия неспецифической хирургической инфекции: Автореф. … дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. - Москва, 1972. - 34 с.
8. Ефименко Н.А., Новожилов А.А., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Системная энзимотерапия в гнойной хирургии // Амбулаторная хирургия. - 2005. - №3. - С. 51-55.
9. Заря О.И. Обоснование использования иммобилизированных протеолитических ферментов в лечебно-профилактических зубных пастах: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Омск, 1994. - 20 с.
10. Использование энзимных препаратов в хирургической стоматологии и челюстно-лицевой хирургии: Методические рекомендации. Сост.: Дрегалкина А.А., Васильева Е.С. - Екатеринбург: УГМА, 2003. - 25 с.
11. Корчак Л.Ф. Применение ферментов протеолиза в лечении одонтогенных воспалительных процессов челюстно-лицевой области: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Киев, 1972. - 30 с.
12. Котельников Г.П., Труханова И.Г., Труханов В.В. Возможности коррекции иммунных нарушений при челюстно-лицевой травме // Тез. докл. Всеросс. конф. с международным участием “Проблемы реабилитации в оториноларингологии”. - Самара, 2003. - С. 56-57.
13. Кошкин В.М., Минаев С.В., Спесивцев Ю.А., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Полиферментные препараты в хирургической практике. - СПб.: Человек, 2004. – 112 с.
14. Кузьмина Э.М., Иванов В.Н., Иванова Е.Н. и др. Ферменты в предупреждении кариеса зубов // Новое в стоматологии. - 1996. - № 1. - С. 34-36.
15. Любенко О.Г., Москвичев В.Е., Родин Р.Ю., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Системная энзимотерапия при острых состояниях в стоматологии // Стоматолог. - 2007. - №12. - С. 58-61.
16. Минаев С.В., Ибрагимов О.Р., Зеленский В.А., Минаева Н.В. Улучшение результатов лечения больных с гнойно-воспалительными заболеваниями в челюстно-лицевой хирургии // Военно-Медицинский журнал. - 2007. - №11. - С. 52-58.
17. Минаев С.В., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Технология системной энзимотерапии в хирургической практике // Амбулаторная хирургия. - 2007. - №2 (26). - С. 89-92.
18. Мнацакалян Э.А. Применение протеолитических ферментов в лечении острых гнойных периодонтитов и острых гнойных периоститов. // Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. - Ереван, 1971.
19. Непомнящая Н.В., Гильмияров Э.М., Постников М.А. Комплексное лечение хронического пародонтита у пациентов с зубочелюстными аномалиями в зависимости от групповой принадлежности крови. // Стоматологический Вестник Поволжья. - 2009. - №1 (16). - С. 8-10.
20. Притыко А.Г., Балакирева Г.М., Мкртумян Э.С. и др. Опыт применения препарата Вобэнзим при костной пластике врожденной расщелины альвеолярного отростка верхней челюсти у детей // J. of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. - 1998. Vol. 26 (Suppl. 1). №8. P. 106.
21. Притыко А.Г., Лопатин А.В., Гончаков Г.В. Применение Флогэнзима и Вобэнзима в клинике детской черепно-лицевой хирургии // Мат. науч.-практ. конф. “Новые аспекты системной энзимотерапии”. - М., 2001. - С. 147-151.
22. Прудникова О.В. Разработка и обоснование методовлечения хронического периодонтита с применением литического ферментного препарата лизоамидазы: Автореф. дис. ... канд. мед. наук. - М. - 1997.
23. Ремезов А.П., Кнорринг Г.Ю. Cистемная энзимотерапия как способ потенцирования антибактериальных средств // Антибиотики и химиотерапия. - 2003. - Т. 48. №3. - С. 30-33.
24. Abbott P.V., Hume W.R., Pearman J.W. Antibiotics and endodontics. Austral Dental J 1990; 35: 50-60.
25. Navrátilová B., Navrátil L. Use of systemic enzyme therapy in stomatology - current options (preliminary study). Miniinvazivní terapie - 1998, №3. - str. 106-109.
26. Vinzenz K. Edema therapy in dental interventions with hydrolytic enzymes. [Odembehandlung bei zahnchirurgischen Eingriffen mit hydrolytischen Enzymen] Quintessenz. 1991: 42 (7):1053-1064.
| Авторы: | Стернин Ю.И., Кнорринг Г.Ю., Любенко О.Г., Мамедов С.С. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 52-54 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Гиперчувствительность дентина — внезапная кратковременная боль в областиобнаженного дентина зуба, не связанная с какой-либо явной патологией зубов. Проблема гиперчувствительности требует серьезного внимания, поскольку имеет высокую распространенность и снижает качество жизни человека. В статье обсуждаются основные факторы риска, связанные с гиперчувствительностью.
Предложено несколько теорий, объясняющих механизм развития гиперчувствительности дентина. Наиболее распространенной является гидродинамическая теория, дополненная теорией раздражения нервных окончаний в пульпе за счет передачи электропотенциалов. Способы борьбы с гиперчувствительностью включают широкий спектр технологий: от средств-десенситайзеров для домашнего и профессионального применения до механической изоляции поверхности дентина адгезивными материалами. Принцип действия применяемых в клинической практике десенситайзеров основан либо на обтурации просвета открытых дентинных канальцев, либона деполяризующем эффекте ионов калия со снижением проводимости нервного импульса. В целом оптимального средства, отвечающего всем требованиям клинической практики, на сегодняшний день не существует, а поиск новых средств для борьбы с гиперчувствительностью дентина остается актуальной задачей для стоматологии. Среди последних предложений особое внимание привлекает новая технология, основанная на сочетанном применении аминокислоты аргинина и минерального комплекса. Пилотные исследования и опыт клинического применения подтвержают, что инновационная технология, основанная на комплексе “аргинин/карбонат кальция”, обеспечивает достижение быстрого и стойкого эффекта устранения гиперчувствительности дентина.
Ключевые слова: гиперчувствительность дентина, клиника, этиология, десенситайзер, обзор.
Dentin hypersensitivity: clinical problem and solutions.
Summary. Dentin hypersensitivity is distinguished as a sudden pain arising from exposed dentin that cannot be explained by any other form of dental pathology. Dentin hypersensitivity is a common problem in adult populations, and it may decrease the quality of life. Main risk factors connected with dentin hypersensitivity are discussed in the publication. Several theories have been proposed over the years to explain the mechanism of dentin hypersensitivity. The hydrodynamic theory is generally favored by the dental community to explain hypersensitivity, added by theory of direct stimulation of the nerves within the pulp via electrical current. The clinical management of the condition varies widely from everyday home use products, like desensitizing toothpastes up to the products that are applied by the dental professional in office, such as varnishes (resins). Main approaches of desensitizing are to limit the possibility of fluid displacement within dentin tubules or to provide depolarizing effect on electrical nerve conduction. Not any of traditional products are sufficient yet, so the search of “ideal” desensitizing product is still open. One of novel breaking-through technology is a formula based on amino acid Arginine combined with mineral complex. Pilot studies and clinical experience demonstrate that innovative technology based on “arginine/calcium carbonate” results in fast and stable release of dentine hypersensitivity.
Key words: dentin hypersensitivity, clinical features; etiology; desensitizing treatments; review.
Литература:
1. Markowitz K, Pashley DH: Discovering new treatments for sensitive teeth: The long path from biology to therapy. J Oral Rehabil 35:300-315, 2008.
2. Gillam DG, Seo HS, Bulman JS, Newman HN. Perceptions of dentine hypersensitivity in a general practice population J Oral Rehabil 1999;26:710-4.
3. Schuurs AH, Wesselink PR, Eijkman MA, DuivenvoordenHJ. Dentists’ views on cervical hypersensitivity and their knowledge of its treatment. Endod Dent Traumatol 1995;11:240-4.
4. Fischer C, Fischer R G, Wennberg A. Prevalence and distribution of cervical dentine hypersensitivity in a population in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil J Dent 1992; 20: 272-276.
5. Irwin C R, McCusker P. Prevalence of dentine hypersensitivity in a general dental population.J Irish Dent Assoc 1997; 43: 7-9.
6. Liu H C, Lan W H, Hsieh C C. Prevalence and distribution of cervical dentin hypersensitivity in a population in Taipei, TaiwanJ Endodont 1998; 24: 45-47.)
7. Dababneh RH, Khouri AT, Addy M.Dentine hypersensitivity - an enigma? A review of terminology, mechanisms, aetiology and management. Br Dent J, 1999- 11;187(11):606-611
8. Addy M, Embery G, Edgar WM, Orchardson R, eds. Tooth wear and sensitivity: Clinical advances in restorative dentistry. London: Martin Dunitz; 2000:239-48
9. Orchardson R, Collins WJ. Br Dent J 1987;162:253-6, Addy M, Mostafa P, Newcombe RG. J Dent 1987;15:242-8.
10. Orchardson R, Collins WJ. Clinical features of hypersensitive teeth. Br Dent J 1987;162:253-6.
11. Addy M, Hunter ML: Can tooth brushing damage your health? Effects on oral and dental tissues. Int Dent J 2003;53(suppl 3):177-186.
12. Yoshiyama M, Noiri Y, Ozaki K, Uchida A, Ishikawa Y, Ishida H. Transmission electron microscopic characterization of hypersensitive human radicular dentin. J Dent Res 1990;69:1293-7
13. Al-Wahadni A, Linden GJ. Dentine hypersensitivity in Jordanian dental attenders: a case control study. J Clin Periodontol 2002;29: 688-93
14. Rees JS, Jin LJ, Lam S, Kudanowska I, Vowles R. The prevalence of dentin hypersensitivity in a hospital clinic population in Hong Kong. J Dent 2003;31:453-61
15. von Troil B, Needleman I, Sanz M. A systematic review ofthe prevalence of root sensitivity following periodontaltherapy Journal Of Clinical Periodontology. - J Clin Periodontol 2002;29(supplement 3):173-7;
16. Kleinberg I. Sensitstat. A new saliva-based composition forsimple and effective treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity. Dent Today 2002; 21:42-47.
17. Schiff T, Delgado E, Zhang YP, DeVizio W, Mateo LR. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of a desensitizing paste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate in providing instant and lasting in-office relief of dentin hypersensitivity. Am J Dent 2009; 22 (Sp Is A):8A-15A.
18. Hamlin D, Williams KP, Delgado E, Zhang YP, DeVizio W, Mateo LR. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of a desensitizing paste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate for the in-office relief of dentin hypersensitivity associated with dental prophylaxis. Am J Dent 2009; 22 (Sp Is A):16A-20A.
Предложено несколько теорий, объясняющих механизм развития гиперчувствительности дентина. Наиболее распространенной является гидродинамическая теория, дополненная теорией раздражения нервных окончаний в пульпе за счет передачи электропотенциалов. Способы борьбы с гиперчувствительностью включают широкий спектр технологий: от средств-десенситайзеров для домашнего и профессионального применения до механической изоляции поверхности дентина адгезивными материалами. Принцип действия применяемых в клинической практике десенситайзеров основан либо на обтурации просвета открытых дентинных канальцев, либона деполяризующем эффекте ионов калия со снижением проводимости нервного импульса. В целом оптимального средства, отвечающего всем требованиям клинической практики, на сегодняшний день не существует, а поиск новых средств для борьбы с гиперчувствительностью дентина остается актуальной задачей для стоматологии. Среди последних предложений особое внимание привлекает новая технология, основанная на сочетанном применении аминокислоты аргинина и минерального комплекса. Пилотные исследования и опыт клинического применения подтвержают, что инновационная технология, основанная на комплексе “аргинин/карбонат кальция”, обеспечивает достижение быстрого и стойкого эффекта устранения гиперчувствительности дентина.
Ключевые слова: гиперчувствительность дентина, клиника, этиология, десенситайзер, обзор.
Dentin hypersensitivity: clinical problem and solutions.
Summary. Dentin hypersensitivity is distinguished as a sudden pain arising from exposed dentin that cannot be explained by any other form of dental pathology. Dentin hypersensitivity is a common problem in adult populations, and it may decrease the quality of life. Main risk factors connected with dentin hypersensitivity are discussed in the publication. Several theories have been proposed over the years to explain the mechanism of dentin hypersensitivity. The hydrodynamic theory is generally favored by the dental community to explain hypersensitivity, added by theory of direct stimulation of the nerves within the pulp via electrical current. The clinical management of the condition varies widely from everyday home use products, like desensitizing toothpastes up to the products that are applied by the dental professional in office, such as varnishes (resins). Main approaches of desensitizing are to limit the possibility of fluid displacement within dentin tubules or to provide depolarizing effect on electrical nerve conduction. Not any of traditional products are sufficient yet, so the search of “ideal” desensitizing product is still open. One of novel breaking-through technology is a formula based on amino acid Arginine combined with mineral complex. Pilot studies and clinical experience demonstrate that innovative technology based on “arginine/calcium carbonate” results in fast and stable release of dentine hypersensitivity.
Key words: dentin hypersensitivity, clinical features; etiology; desensitizing treatments; review.
Литература:
1. Markowitz K, Pashley DH: Discovering new treatments for sensitive teeth: The long path from biology to therapy. J Oral Rehabil 35:300-315, 2008.
2. Gillam DG, Seo HS, Bulman JS, Newman HN. Perceptions of dentine hypersensitivity in a general practice population J Oral Rehabil 1999;26:710-4.
3. Schuurs AH, Wesselink PR, Eijkman MA, DuivenvoordenHJ. Dentists’ views on cervical hypersensitivity and their knowledge of its treatment. Endod Dent Traumatol 1995;11:240-4.
4. Fischer C, Fischer R G, Wennberg A. Prevalence and distribution of cervical dentine hypersensitivity in a population in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil J Dent 1992; 20: 272-276.
5. Irwin C R, McCusker P. Prevalence of dentine hypersensitivity in a general dental population.J Irish Dent Assoc 1997; 43: 7-9.
6. Liu H C, Lan W H, Hsieh C C. Prevalence and distribution of cervical dentin hypersensitivity in a population in Taipei, TaiwanJ Endodont 1998; 24: 45-47.)
7. Dababneh RH, Khouri AT, Addy M.Dentine hypersensitivity - an enigma? A review of terminology, mechanisms, aetiology and management. Br Dent J, 1999- 11;187(11):606-611
8. Addy M, Embery G, Edgar WM, Orchardson R, eds. Tooth wear and sensitivity: Clinical advances in restorative dentistry. London: Martin Dunitz; 2000:239-48
9. Orchardson R, Collins WJ. Br Dent J 1987;162:253-6, Addy M, Mostafa P, Newcombe RG. J Dent 1987;15:242-8.
10. Orchardson R, Collins WJ. Clinical features of hypersensitive teeth. Br Dent J 1987;162:253-6.
11. Addy M, Hunter ML: Can tooth brushing damage your health? Effects on oral and dental tissues. Int Dent J 2003;53(suppl 3):177-186.
12. Yoshiyama M, Noiri Y, Ozaki K, Uchida A, Ishikawa Y, Ishida H. Transmission electron microscopic characterization of hypersensitive human radicular dentin. J Dent Res 1990;69:1293-7
13. Al-Wahadni A, Linden GJ. Dentine hypersensitivity in Jordanian dental attenders: a case control study. J Clin Periodontol 2002;29: 688-93
14. Rees JS, Jin LJ, Lam S, Kudanowska I, Vowles R. The prevalence of dentin hypersensitivity in a hospital clinic population in Hong Kong. J Dent 2003;31:453-61
15. von Troil B, Needleman I, Sanz M. A systematic review ofthe prevalence of root sensitivity following periodontaltherapy Journal Of Clinical Periodontology. - J Clin Periodontol 2002;29(supplement 3):173-7;
16. Kleinberg I. Sensitstat. A new saliva-based composition forsimple and effective treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity. Dent Today 2002; 21:42-47.
17. Schiff T, Delgado E, Zhang YP, DeVizio W, Mateo LR. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of a desensitizing paste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate in providing instant and lasting in-office relief of dentin hypersensitivity. Am J Dent 2009; 22 (Sp Is A):8A-15A.
18. Hamlin D, Williams KP, Delgado E, Zhang YP, DeVizio W, Mateo LR. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of a desensitizing paste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate for the in-office relief of dentin hypersensitivity associated with dental prophylaxis. Am J Dent 2009; 22 (Sp Is A):16A-20A.
| Авторы: | Соловьева А.М. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 48-51 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Зона улыбки предъявляет особые требования к эстетике реставраций, делая в рядеслучаев невозможным применение полноценного армирования с помощью жгутов или лент. При этом, если композитная конструкция без волоконного усиления оказывается несостоятельна, возможным компромиссом является применение тончайшей стекловолоконной сетки everStick NET от компании Stick Tech. В данной статье объединены клинические случаи применения подобного армирования в повседневной стоматологической практике.
Ключевые слова: волоконное армирование, волоконная сетка, Stick Tech, everStick NET, сколы режущего края, армирование резцовой трети, шинирование при травме, починка виниров.
Fiber reinforcement in everyday dentistry. Part 3. Reinforcement of frontal teeth (T.S.Dvornikova, P.h.D. D.D.S., associated professor, chief dentist).
Summary. Frontal teeth are especially sensitive to the aesthetics of the restorations, which makes impossible in some cases the traditional reinforcement with fiber bundles or bands. However, if the composite restoration without fiber reinforcement is ineffective, thin fiberglass net could be used instead. This article contains the joint description of clinical cases involving the everStick Net (Stick Tech) reinforcement technique in everyday dental practice.
Key words: FRC, IPN, fiberglass net, Stick Tech, everStick NET, reinforcement of IV class restorations, veneer reinforcement, veneer repairing, trauma splinting.
Литература:
1. Антонов М.Е. Метод замещения единичной потери зуба. - Автореф. дисс. канд. мед. наук. - М., 1999. - 16 с.
2. Борисенко А.В. Секреты лечения кариеса и реставрации зубов. - М.: Книга плюс, 2002. - 544 с.
3. Борисенко А.В. Ошибки и осложнения, возникающие при использовании композиционных материалов // Современная стоматология. - 1999. - №2. - С. 8-11.
4. Иоффе Е. Зубоврачебные заметки. - Нью-Йорк-анкт-Петербург, 1999. - 215 с.
5. Макеева И.М. Восстановление зубов светоотверждаемыми композитными материалами.- М.: ОАО “Стоматология”, 1997. - 72 с.
6. Макеева И.М., Шелеметьева Г.Н., Туркина А.Ю. Отдалённые результаты восстановления фронтальных зубов композитными материалами светового отверждения // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 5. - С. 41-44.
7. Мусихина Е.В. Клинико-лабораторное исследование армирования при пломбированиидефектов режущего края и окклюзионной поверхности зубов. - Автореф. дисс. канд. мед. наук. - М., 2005. - 16 с.
8. Николаев А.И. Цепов Л.М. Практическая терапевтическая стоматология: Учебное пособие.- М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2008. - 960 с.
9. Николишин А.К. Восстановление (реставрация) и пломбирование зубов современными материалами и технологиями. - Полтава, 2001. - 176 с.
10. Радлинская В.Н., Радлинский С.В. Современные технологии реставрации зубов. - Полтава, 2002. - 59 с.
11. Радлинский С.В. Восстановление длины передних зубов // Дент Арт. - 2003. - №1. - С. 27-38.
12. Салова А.В., Рехачев В.М. Особенности эстетической реставрации в стоматологии: Практическое руководство. - СПб.: Человек, 2003. - 112 с.
13. Чиликин В.Н. Новейшие технологии в эстетической стоматологии. - М.,: МЕДпресс-информ, 2004. - 96 с.
14. Хельвиг Э., Климек Й., Аттин Т. Терапевтическая стоматология. Пер. с нем.. - Львов: ГалДент, 1999, - 409 с.
15. Lastumäki T.M., Lassila L.V., Vallitu P.K. The semiinterpenetrating polymer network matrix of fiberreinforced composite and its effect on the surface adhesive properties.- J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. - 2003 Sep; 14(9), Р. 803-809.
Ключевые слова: волоконное армирование, волоконная сетка, Stick Tech, everStick NET, сколы режущего края, армирование резцовой трети, шинирование при травме, починка виниров.
Fiber reinforcement in everyday dentistry. Part 3. Reinforcement of frontal teeth (T.S.Dvornikova, P.h.D. D.D.S., associated professor, chief dentist).
Summary. Frontal teeth are especially sensitive to the aesthetics of the restorations, which makes impossible in some cases the traditional reinforcement with fiber bundles or bands. However, if the composite restoration without fiber reinforcement is ineffective, thin fiberglass net could be used instead. This article contains the joint description of clinical cases involving the everStick Net (Stick Tech) reinforcement technique in everyday dental practice.
Key words: FRC, IPN, fiberglass net, Stick Tech, everStick NET, reinforcement of IV class restorations, veneer reinforcement, veneer repairing, trauma splinting.
Литература:
1. Антонов М.Е. Метод замещения единичной потери зуба. - Автореф. дисс. канд. мед. наук. - М., 1999. - 16 с.
2. Борисенко А.В. Секреты лечения кариеса и реставрации зубов. - М.: Книга плюс, 2002. - 544 с.
3. Борисенко А.В. Ошибки и осложнения, возникающие при использовании композиционных материалов // Современная стоматология. - 1999. - №2. - С. 8-11.
4. Иоффе Е. Зубоврачебные заметки. - Нью-Йорк-анкт-Петербург, 1999. - 215 с.
5. Макеева И.М. Восстановление зубов светоотверждаемыми композитными материалами.- М.: ОАО “Стоматология”, 1997. - 72 с.
6. Макеева И.М., Шелеметьева Г.Н., Туркина А.Ю. Отдалённые результаты восстановления фронтальных зубов композитными материалами светового отверждения // Стоматология. - 2002. - № 5. - С. 41-44.
7. Мусихина Е.В. Клинико-лабораторное исследование армирования при пломбированиидефектов режущего края и окклюзионной поверхности зубов. - Автореф. дисс. канд. мед. наук. - М., 2005. - 16 с.
8. Николаев А.И. Цепов Л.М. Практическая терапевтическая стоматология: Учебное пособие.- М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2008. - 960 с.
9. Николишин А.К. Восстановление (реставрация) и пломбирование зубов современными материалами и технологиями. - Полтава, 2001. - 176 с.
10. Радлинская В.Н., Радлинский С.В. Современные технологии реставрации зубов. - Полтава, 2002. - 59 с.
11. Радлинский С.В. Восстановление длины передних зубов // Дент Арт. - 2003. - №1. - С. 27-38.
12. Салова А.В., Рехачев В.М. Особенности эстетической реставрации в стоматологии: Практическое руководство. - СПб.: Человек, 2003. - 112 с.
13. Чиликин В.Н. Новейшие технологии в эстетической стоматологии. - М.,: МЕДпресс-информ, 2004. - 96 с.
14. Хельвиг Э., Климек Й., Аттин Т. Терапевтическая стоматология. Пер. с нем.. - Львов: ГалДент, 1999, - 409 с.
15. Lastumäki T.M., Lassila L.V., Vallitu P.K. The semiinterpenetrating polymer network matrix of fiberreinforced composite and its effect on the surface adhesive properties.- J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. - 2003 Sep; 14(9), Р. 803-809.
| Авторы: | Дворникова Т.С. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 44-47 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Проведен анализ 122 случаев лечения неклостридиальных анаэробных флегмон лица и шеи и их осложнений, определен превалирующий состав микрофлоры, вызывающей воспалительные процессы челюстно-лицевой области и шеи. Предложены алгоритмы диагностики и лечения заболеваний, вызванных неклостридиальной анаэробной инфекцией.
Ключевые слова: неклостридиальный, анаэробный, инфекция.
Diagnostics and treatment of the anaerobic non-clostridial inflammantions maxillofacial region and neck (A.A.Oganesyan, B.V.Trifonov).
Summary. 122 cases of treatment of nonclostridial anaerobic phlegmons of the maxillofacial and neck area and their complications were analyzed. The prevailing structure of the microflora causing inflammatory processes of maxillofacial area and a neck is defined. New algorithms of diagnostics and treatment of non-clostridial anaerobic infection are offered.
Key words: non-clostridial, anaerobic, inflammations.
Литература:
1. Губин М.А. Анализ результатов диагностики и лечения сепсиса у стоматологических больных/ М.А.Губин, Ю.М.Харитонов, Н.Л.Елькова // Системный анализ и управление в биомедицинских системах: журнал практической и теоретической биологии и медицины РАЕН им. Вернадского. - М. - 2004. - Том 3, №1. - С. 57-60.
2. Кузьмин Ю.В. Диагностика и лечение анаэробнойнеклостридиальной инфекции мягких тканей: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук - Минск, 2001. - 20 с.
3. Одонтогенные воспалительные заболевания: Руководство для врачей. / Под ред. Т.Г.Робустовой. - М., - 2006. - 664 с.
4. Робустова Т.Г. Динамика частоты и тяжестиодонтогенных воспалительных заболеваний за 50 лет (1955-2004). // Стоматология. - 2007. - №3. - С. 63-66.
5. Серажим О.А. Комплексное лечение анаэробной неклостридиальной инфекции мягких тканей: Дис. … канд. мед. наук - М., 2004. - 135 с.
Ключевые слова: неклостридиальный, анаэробный, инфекция.
Diagnostics and treatment of the anaerobic non-clostridial inflammantions maxillofacial region and neck (A.A.Oganesyan, B.V.Trifonov).
Summary. 122 cases of treatment of nonclostridial anaerobic phlegmons of the maxillofacial and neck area and their complications were analyzed. The prevailing structure of the microflora causing inflammatory processes of maxillofacial area and a neck is defined. New algorithms of diagnostics and treatment of non-clostridial anaerobic infection are offered.
Key words: non-clostridial, anaerobic, inflammations.
Литература:
1. Губин М.А. Анализ результатов диагностики и лечения сепсиса у стоматологических больных/ М.А.Губин, Ю.М.Харитонов, Н.Л.Елькова // Системный анализ и управление в биомедицинских системах: журнал практической и теоретической биологии и медицины РАЕН им. Вернадского. - М. - 2004. - Том 3, №1. - С. 57-60.
2. Кузьмин Ю.В. Диагностика и лечение анаэробнойнеклостридиальной инфекции мягких тканей: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук - Минск, 2001. - 20 с.
3. Одонтогенные воспалительные заболевания: Руководство для врачей. / Под ред. Т.Г.Робустовой. - М., - 2006. - 664 с.
4. Робустова Т.Г. Динамика частоты и тяжестиодонтогенных воспалительных заболеваний за 50 лет (1955-2004). // Стоматология. - 2007. - №3. - С. 63-66.
5. Серажим О.А. Комплексное лечение анаэробной неклостридиальной инфекции мягких тканей: Дис. … канд. мед. наук - М., 2004. - 135 с.
| Авторы: | Оганесян А.А., Трифонов Б.В. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 42-43 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. В статье представлены результаты клинического применения биополимерных пленок с иммунокорректором имудоном для пациентов, пользующихся съемными протезами. Были достигнуты положительные эффекты, такие как: повышение резистентности слизистой оболочки к негативному действию съемного протеза, улучшение местного иммунитета полости рта, сокращение сроков адаптации, повышение функциональной эффективности зубочелюстной системы и улучшение качества жизни пациентов с полным или частичным отсутствием зубов.
Ключевые слова: иммунокоректор, имудон, биополимерная пленка, протез.
Evaluation of application efficiency of themedicated films containing immunocorrector in removable prosthetics (E.S.Kalivradjiyan, Doctor of medical sciences, Professor; E.A.Leshcheva, Doctor of medical sciences, Professor; N.V.Primacheva, post-graduate; N.V. Chirkova, Candidate of medical sciences, teacher, Department of orthopedic stomatology, Voronezh State Medical Academy named after N.N.Burdenko).
Summary. The article presents the results of clinical application of biopolymer films with immunocorrector — immudone for the patients using protheses. Positive effects were achieved such as an increase of resistancy of the mucous shell to the negative effect of prothesis, improvement of the local immunity of dentalvealveolar system reduce of adaptation terms, increase of the functional efficiency of the tooth-system and improvement of the life quality of the patients with partial or completely absent teeth.
Key words: immunocorrector, immudone, biopolymer films, prothesis.
Литература:
1. Шевченко О.В. Состояние слизистой оболочки полости рта под влиянием частичных съемных пластиночных протезов. / О.В.Шевченко; Тверская гос. мед. акад. - Тверь, 2004. -17 с.
2. Биорастворимые лекарственные пленки - эффективное средство аппликационной анестезии в стоматологии. / Л.Н.Олешко [и др.] // Научная ссесия ЦНИИС, посвященая 35-летию института: М., 1998. - С. 188-192.
3. Пан Е.Г. Применение иммунокорригирующихпрепаратов у пациентов, пользующихся съемными зубными протезами. / Е.Г. Пан, А.Н.Емельянов // Клиническая стоматология. - 2004. - №3. - С. 62.
4. Бачимова К.К. Разработка и клинико-лабораторное обоснование применения стоматологической пленки “Диплен-КП” при лечении хронического пародонтита: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. / К.К.Бачимова; МГМСУ. - М., 2004. - 26 с.
5. Шумский А.В. Имудон в лечении ифекционно-воспалительных заболеваний слизистой оболочки полости рта. / А.В.Шумский // Стоматология. - 2000. - т. 79, №6. - С. 53-55.
6. Использование регистрирующей компьютернойсистемы обработки изображений для оценки функционального состояния зубочелюстной системы / Каливраджиян Э.С. [и др.] // Материалы Х1Х и ХХ Всероссийской научно-практической конференции. - Москва, 2008. - С. 431.
7. Каливраджиян Э.С. Способ выявления перегрузки тканей под базисом съемного протеза / Н.И.Лесных // Стомтология. - 1987. - № 6. - С. 55-57.
Ключевые слова: иммунокоректор, имудон, биополимерная пленка, протез.
Evaluation of application efficiency of themedicated films containing immunocorrector in removable prosthetics (E.S.Kalivradjiyan, Doctor of medical sciences, Professor; E.A.Leshcheva, Doctor of medical sciences, Professor; N.V.Primacheva, post-graduate; N.V. Chirkova, Candidate of medical sciences, teacher, Department of orthopedic stomatology, Voronezh State Medical Academy named after N.N.Burdenko).
Summary. The article presents the results of clinical application of biopolymer films with immunocorrector — immudone for the patients using protheses. Positive effects were achieved such as an increase of resistancy of the mucous shell to the negative effect of prothesis, improvement of the local immunity of dentalvealveolar system reduce of adaptation terms, increase of the functional efficiency of the tooth-system and improvement of the life quality of the patients with partial or completely absent teeth.
Key words: immunocorrector, immudone, biopolymer films, prothesis.
Литература:
1. Шевченко О.В. Состояние слизистой оболочки полости рта под влиянием частичных съемных пластиночных протезов. / О.В.Шевченко; Тверская гос. мед. акад. - Тверь, 2004. -17 с.
2. Биорастворимые лекарственные пленки - эффективное средство аппликационной анестезии в стоматологии. / Л.Н.Олешко [и др.] // Научная ссесия ЦНИИС, посвященая 35-летию института: М., 1998. - С. 188-192.
3. Пан Е.Г. Применение иммунокорригирующихпрепаратов у пациентов, пользующихся съемными зубными протезами. / Е.Г. Пан, А.Н.Емельянов // Клиническая стоматология. - 2004. - №3. - С. 62.
4. Бачимова К.К. Разработка и клинико-лабораторное обоснование применения стоматологической пленки “Диплен-КП” при лечении хронического пародонтита: Автореф. дис. … канд. мед. наук. / К.К.Бачимова; МГМСУ. - М., 2004. - 26 с.
5. Шумский А.В. Имудон в лечении ифекционно-воспалительных заболеваний слизистой оболочки полости рта. / А.В.Шумский // Стоматология. - 2000. - т. 79, №6. - С. 53-55.
6. Использование регистрирующей компьютернойсистемы обработки изображений для оценки функционального состояния зубочелюстной системы / Каливраджиян Э.С. [и др.] // Материалы Х1Х и ХХ Всероссийской научно-практической конференции. - Москва, 2008. - С. 431.
7. Каливраджиян Э.С. Способ выявления перегрузки тканей под базисом съемного протеза / Н.И.Лесных // Стомтология. - 1987. - № 6. - С. 55-57.
| Авторы: | Каливраджиян Э.С., Примачёва Н.В., Лещева Е.А., Чиркова Н.В. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 40-41 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. По сопоставленным данным патоморфологии и оптической плотности челюсти при гингивите,пародонтите, различных видах пародонтопатии делается вывод о необходимости и возможности скринингового исследования кости нижней челюсти (особенно при ортопантомографии) на предмет определения плотности костной ткани для прогнозирования течения пародонтита. Указанные измерения становятся наиболее рациональными при цифровой рентгенографии.
Ключевые слова: оптическая плотность костной ткани, пародонтит.
Density of lower jaw bony tissue in screening of parodontium (V.M. SCHerbich, S.N.Moscovskiy, V.P.Konev, A.F.Sulimov).
Summary. On comparable given pathological morphology and absorbances to jaws at gingivitis, periodontitis, different type periodontopathy, is done conclusion about need and possibility screening studies to bones to mandible (particularly under ontopantomographyti) on subject of the determination to density bone fabrics for forecasting of the current periodontitis. The Specified measurements become the most rational under digital radiology.
Key words: absorbances bone fabrics, periodontitis.
Литература:
1. Трофимова Т.Н., Гарапач И.А., Цимбалистов А.В.и др. Рентгенометрические характеристики нижней челюсти у больных генерализованным пародонтитом и системным остеопорозом // Пародонтология. - 2005 - №2, т. 35. - С. 23-26.
2. Семенюк В.М., Яковлев К.К. Современные аспекты диагностики и лечения заболеваний пародонта в клинике ортопедической стоматологии // Методическое указание. - Омск, 1997. - 15 с.
3. Дунязина Т.Н., Калинина Н.М., Никифорова И.Д. Современные методы диагностики заболеваний пародонта. - СПб.: МЕДИ, 2001. - 48 с.
4. Курякина Н.В., Кутепова Т.Ф. Заболевания пародонта. - М.: Медицинская книга. - Н.Новгород: НГМА, 2000 - 162 с.
5. Dawson Hughes B. Vitamin D and calcium. Recommended intake for bone health. // Osteoporosis Int.,1998;8 (Suppl. 2): 30 34.
6. Bracker MD, Watts NB. How to get the most out of bone densitometry. Results can help assess fracture risk and guide therapy. Postgrad Med 1998; 104: 77-9,83-6.
7. Miller PD, Zapalowski C, Kulak CA, Bilezikian JP. Bone densitometry: the best way to detect osteoporosis and to monitor therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84:1867-71.
8. Machann J., Schnatterbeck P., Raible A. et al. Magnetic resonance osteodensitometry in human heel bones: correlation with quantitative computed to mography using different measuring parameters. // Invest. Radiol. - 2000. - №35. - Vol. 7. - P. 393-400.
Ключевые слова: оптическая плотность костной ткани, пародонтит.
Density of lower jaw bony tissue in screening of parodontium (V.M. SCHerbich, S.N.Moscovskiy, V.P.Konev, A.F.Sulimov).
Summary. On comparable given pathological morphology and absorbances to jaws at gingivitis, periodontitis, different type periodontopathy, is done conclusion about need and possibility screening studies to bones to mandible (particularly under ontopantomographyti) on subject of the determination to density bone fabrics for forecasting of the current periodontitis. The Specified measurements become the most rational under digital radiology.
Key words: absorbances bone fabrics, periodontitis.
Литература:
1. Трофимова Т.Н., Гарапач И.А., Цимбалистов А.В.и др. Рентгенометрические характеристики нижней челюсти у больных генерализованным пародонтитом и системным остеопорозом // Пародонтология. - 2005 - №2, т. 35. - С. 23-26.
2. Семенюк В.М., Яковлев К.К. Современные аспекты диагностики и лечения заболеваний пародонта в клинике ортопедической стоматологии // Методическое указание. - Омск, 1997. - 15 с.
3. Дунязина Т.Н., Калинина Н.М., Никифорова И.Д. Современные методы диагностики заболеваний пародонта. - СПб.: МЕДИ, 2001. - 48 с.
4. Курякина Н.В., Кутепова Т.Ф. Заболевания пародонта. - М.: Медицинская книга. - Н.Новгород: НГМА, 2000 - 162 с.
5. Dawson Hughes B. Vitamin D and calcium. Recommended intake for bone health. // Osteoporosis Int.,1998;8 (Suppl. 2): 30 34.
6. Bracker MD, Watts NB. How to get the most out of bone densitometry. Results can help assess fracture risk and guide therapy. Postgrad Med 1998; 104: 77-9,83-6.
7. Miller PD, Zapalowski C, Kulak CA, Bilezikian JP. Bone densitometry: the best way to detect osteoporosis and to monitor therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84:1867-71.
8. Machann J., Schnatterbeck P., Raible A. et al. Magnetic resonance osteodensitometry in human heel bones: correlation with quantitative computed to mography using different measuring parameters. // Invest. Radiol. - 2000. - №35. - Vol. 7. - P. 393-400.
| Авторы: | Щербич В.М., Московский С.Н., Конев В.П., Сулимов А.Ф. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 38-39 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Необходимость использования дентальных имплантатов для восстановления дефектов зубных рядов в последние годы не вызывает сомнений. Классический метод Бранемарка (1985) подразумевает проведение лечения с использованием имплантатов в несколько этапов, разделенных значительными временными промежутками. Настоящее исследование представляет возможность немедленной имплантации — установки имплантата в лунку зуба непосредственно после его удаления.
Ключевые слова: дентальный имплантат, восстановление, немедленная имплантация.
Immediate Post Extraction Implantation of Dental Implants with Antibacterial Covering (A.V.Lepilin, V.N.Lyasnikov, S.B.Fishchev, A.V.Krasnikov, E.S.Krasnikova, D.A.Smirnov, O.S.Mostovaya).
Summary. Using Dental implants for restoration of defect of the tooth alignment became necessity last years undoubtedly. According to the Classical report of Branemark (1985) treatment with Dental implants includes several stages, divided by considerable time intervals. It is actual Immediate post extraction implantation of Dental Implants.
Key words: dental implants, restoration, immediate implantation.
Литература:
1. Лепилин А.В. Применение эндооссальных цилиндрическихимплантатов с биокерамическим покрытием / А.В.Лепилин, В.Н.Лясников, С.В.Хромых // Тез. докл. 4-й Междунар. конф. “Современные проблемы импланто-логии” (Саратов, 25-27 мая). - Саратов, 1998. - С. 21-22.
2. Лясникова А.В. Современные технологии в производстве высокоэффективных дентальных имплантатов / А.В.Лясникова, К.Г.Бутовский, В.Н.Лясников // Клиническая имплантология и стоматология. - 2003. - №1. - С. 23-24.
3. Albrektsson T.A. A multicenter report on osseointegrated oral implants. J Posthed Dent 1988; 60:75-84.
4. Branemark P.I. Endosteal dental implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw (The Branemark Implant) / P.I. Branemark, T. Albrektsson // In. R. Fronseca, H. Davis Reconstructive preprosthetic oral and maxillofacial surgery. - Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co. - 1985. - 222 р.
5. Broggini N., McManus L.M., Hermann J.S., Medina R., Schenk R.K., Buser D. and Cochran D.L. Peri-implant Inflammation Defined by the Implant-Abutment Interface. Journal of Dental Research, 2006; 85: 473-478.
6. Bücking Wolfram. A Dental Treasure Chest, 2007; 145-160, Quintessence Publishing Co, Ltd, New Madlen, UK.
Ключевые слова: дентальный имплантат, восстановление, немедленная имплантация.
Immediate Post Extraction Implantation of Dental Implants with Antibacterial Covering (A.V.Lepilin, V.N.Lyasnikov, S.B.Fishchev, A.V.Krasnikov, E.S.Krasnikova, D.A.Smirnov, O.S.Mostovaya).
Summary. Using Dental implants for restoration of defect of the tooth alignment became necessity last years undoubtedly. According to the Classical report of Branemark (1985) treatment with Dental implants includes several stages, divided by considerable time intervals. It is actual Immediate post extraction implantation of Dental Implants.
Key words: dental implants, restoration, immediate implantation.
Литература:
1. Лепилин А.В. Применение эндооссальных цилиндрическихимплантатов с биокерамическим покрытием / А.В.Лепилин, В.Н.Лясников, С.В.Хромых // Тез. докл. 4-й Междунар. конф. “Современные проблемы импланто-логии” (Саратов, 25-27 мая). - Саратов, 1998. - С. 21-22.
2. Лясникова А.В. Современные технологии в производстве высокоэффективных дентальных имплантатов / А.В.Лясникова, К.Г.Бутовский, В.Н.Лясников // Клиническая имплантология и стоматология. - 2003. - №1. - С. 23-24.
3. Albrektsson T.A. A multicenter report on osseointegrated oral implants. J Posthed Dent 1988; 60:75-84.
4. Branemark P.I. Endosteal dental implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw (The Branemark Implant) / P.I. Branemark, T. Albrektsson // In. R. Fronseca, H. Davis Reconstructive preprosthetic oral and maxillofacial surgery. - Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co. - 1985. - 222 р.
5. Broggini N., McManus L.M., Hermann J.S., Medina R., Schenk R.K., Buser D. and Cochran D.L. Peri-implant Inflammation Defined by the Implant-Abutment Interface. Journal of Dental Research, 2006; 85: 473-478.
6. Bücking Wolfram. A Dental Treasure Chest, 2007; 145-160, Quintessence Publishing Co, Ltd, New Madlen, UK.
| Авторы: | Лепилин А.В., Лясников В.Н., Фищев С.Б., Красников А.В., Красникова Е.С., Смирнов Д.А., Мостовая О.С. |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 34-37 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)Резюме. Распространенность зубочелюстных аномалий среди подростков и взрослых сегодня составляет более 70%. Нередко причиной нарушения формирования зубных рядов и их смыкания является ретенция отдельных зубов. Несмотря на большую распространенность данной патологии, существует довольно немного методов диагностики положения ретенированных зубов. В данной статье приводится метод диагностики ретенированных зубов по данным дентальной компьютерной томографии.
Ключевые слова: ретенция зубов, методы диагностики, компьютерная томография.
Methods of Evaluation of Retentive Teeth after the Data of Dental Computer Tomography (R.A.Fadeyev, Yu.P.Sheveleva, M.A.Chibisova). Summary. The extent of jaw-dental anomalies upon teenagers and adults makes over 70% today. Often the deformities of dental arches and their occlusion are caused by retention of individual teeth. In spite of great extent of this pathology there are not many methods to diagnose the position of retentive teeth. This article presents a method of diagnostics of retentive teeth with the data of dental computer tomography.
Key words: teeth retention, diagnostic methods, computer tomography.
Литература:
1. Вакушина Е.А., Григоренко П.А. Повышениеэффективности комплексной реабилитациипациентов с ретенцией постоянных зубов // Дентал Юг. - 2009. - №7. - С. 18-21.
2. Степанов Г.В. Клинико-рентгенологическая характеристика при ретенции зубов: учебное пособие. - Самара. - 2008. - 25 с.
3. Фадеев Р.А., Бобров И.П., Кисельникова Л.П., Эрдман О.В. Профилактика зубочелюстных аномалий как условие сохранения здоровья нации // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - №3 (36). - С. 26-27.
4. Чибисова М.А. Возможности клинического использования трехмерного дентального компьютерного томографа 3DX Accuitomo(фирма “Morita”, Япония) // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №2 (31). - С. 98-99.
5. Чибисова М. А. Трехмерный дентальный компьютерный томограф GALILEOS (The Dental Company SIRONA) в амбулаторной стоматологической практике МЕDИ // Институт Стоматологии. - 2008. - №1 (38). - С. 130-131.
6. Чибисова М. А. Повышение качества лечения пациентов при использовании современного рентгенодиагностического комплекса (цифровой панорамный рентгеновский аппарат “Orthophos XG Plus DS/Ceph” с цефалостатом, фирма “Sirona”) в амбулаторной стоматологической практике // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - №4 (37). - С. 120-121.
7. Шигрут Ю. И. План и прогноз лечения при ретенции зубов: Диссертация на соискание ученой степени. - М. - 1994.
Ключевые слова: ретенция зубов, методы диагностики, компьютерная томография.
Methods of Evaluation of Retentive Teeth after the Data of Dental Computer Tomography (R.A.Fadeyev, Yu.P.Sheveleva, M.A.Chibisova). Summary. The extent of jaw-dental anomalies upon teenagers and adults makes over 70% today. Often the deformities of dental arches and their occlusion are caused by retention of individual teeth. In spite of great extent of this pathology there are not many methods to diagnose the position of retentive teeth. This article presents a method of diagnostics of retentive teeth with the data of dental computer tomography.
Key words: teeth retention, diagnostic methods, computer tomography.
Литература:
1. Вакушина Е.А., Григоренко П.А. Повышениеэффективности комплексной реабилитациипациентов с ретенцией постоянных зубов // Дентал Юг. - 2009. - №7. - С. 18-21.
2. Степанов Г.В. Клинико-рентгенологическая характеристика при ретенции зубов: учебное пособие. - Самара. - 2008. - 25 с.
3. Фадеев Р.А., Бобров И.П., Кисельникова Л.П., Эрдман О.В. Профилактика зубочелюстных аномалий как условие сохранения здоровья нации // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - №3 (36). - С. 26-27.
4. Чибисова М.А. Возможности клинического использования трехмерного дентального компьютерного томографа 3DX Accuitomo(фирма “Morita”, Япония) // Институт Стоматологии. - 2006. - №2 (31). - С. 98-99.
5. Чибисова М. А. Трехмерный дентальный компьютерный томограф GALILEOS (The Dental Company SIRONA) в амбулаторной стоматологической практике МЕDИ // Институт Стоматологии. - 2008. - №1 (38). - С. 130-131.
6. Чибисова М. А. Повышение качества лечения пациентов при использовании современного рентгенодиагностического комплекса (цифровой панорамный рентгеновский аппарат “Orthophos XG Plus DS/Ceph” с цефалостатом, фирма “Sirona”) в амбулаторной стоматологической практике // Институт Стоматологии. - 2007. - №4 (37). - С. 120-121.
7. Шигрут Ю. И. План и прогноз лечения при ретенции зубов: Диссертация на соискание ученой степени. - М. - 1994.
| Авторы: | Фадеев Роман Александрович, Шевелёва Ю.П., Чибисова Марина Анатольевна |
| В журнале: | Институт Стоматологии, №46, апрель 2010 |
| Страницы: | 30-33 |
Бесплатно
(в формате  PDF)
PDF)
 PDF)
PDF)